Fluorescence Imaging Device Aids Wound Treatment
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 22 Aug 2018 |
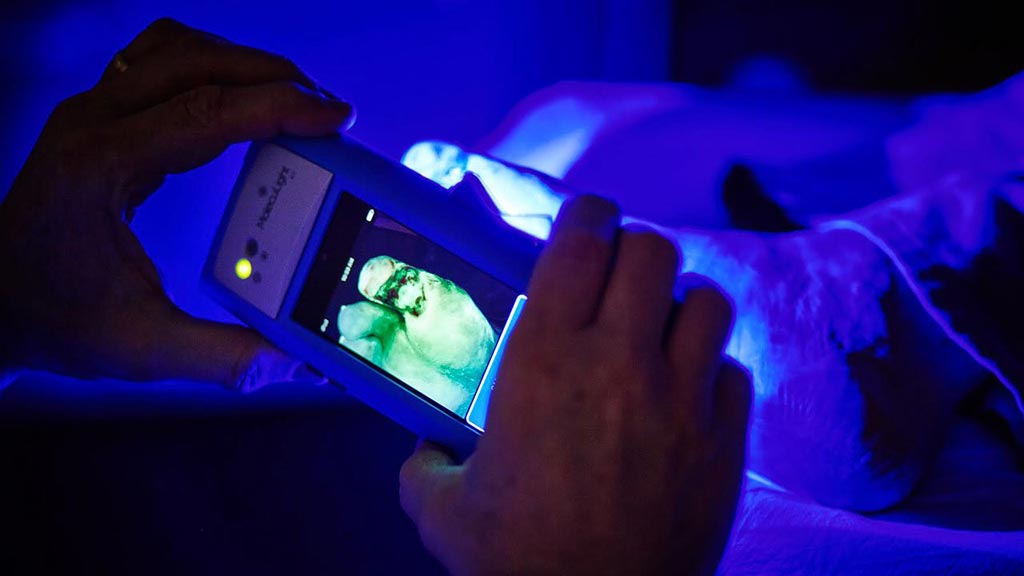

Image: The MolecuLight i:X handheld device uses fluorescence imaging to identify bacteria (Photo courtesy of MolecuLight).
A novel wound imaging device digitally captures and documents fluorescence information from wounds and surrounding tissue using still images and videos in real-time.
The MolecuLight (Toronto, Canada) MolecuLight i:X is intended for point of care (POC) visualization and quantitative tracking of bacterial contamination, wound healing, and connective tissue remodeling of surgical sites and wounds, based on the detection of intrinsic fluorescence signals emitted by tissues and microbes when illuminated with specific wavelengths of light, without the need of contrast agents. Images can be captured and documented as either still images or videos of wounds, including in the surrounding areas where potentially harmful bacteria may be lurking.
MolecuLight i:X emits a precise wavelength of safe violet light, which interacts with the wound tissue and bacteria causing the wound and surrounding skin to emit a green fluorescence, while potentially harmful bacteria emit a red fluorescence. The device captures these red and green fluorescence signals in real time using specialized optical components to filter out the violet light, displaying the resultant image immediately on-screen. The MolecuLight i:X is precisely calibrated to detect fluorescent bacteria at levels higher than 104 CFU/g on a quantitative scale, or predominantly moderate to heavy growth on a semi-quantitative scale.
MolecuLight i:X illuminates the wound with a narrow band of violet light that causes endogenous fluorophores in the bacteria to fluoresce. Susceptible bacteria include Staphylocccus aureus and MRSA; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Escherichia coli; Coagulase-negative staphylococci; multiple Enterococcus species; multiple Proteus species; Klebsiella pneumonia; Beta-hemolytic streptococci (Group B); and multiple Enterobacter species. It is recommended that imaging be performed after surface blood has been removed from the wound bed and peri-wound areas.
“The MolecuLight i:X platform is a significant advancement in the management of chronic wounds that is already revolutionizing wound care practice in Canada and Europe,” said Ralph DaCosta, PhD, founder, director, and chief scientific officer of MolecuLight. “Thousands of patients have already experienced a change in their assessment and treatment by clinicians who feel empowered by the wound fluorescence images they are seeing.”
Related Links:
MolecuLight
The MolecuLight (Toronto, Canada) MolecuLight i:X is intended for point of care (POC) visualization and quantitative tracking of bacterial contamination, wound healing, and connective tissue remodeling of surgical sites and wounds, based on the detection of intrinsic fluorescence signals emitted by tissues and microbes when illuminated with specific wavelengths of light, without the need of contrast agents. Images can be captured and documented as either still images or videos of wounds, including in the surrounding areas where potentially harmful bacteria may be lurking.
MolecuLight i:X emits a precise wavelength of safe violet light, which interacts with the wound tissue and bacteria causing the wound and surrounding skin to emit a green fluorescence, while potentially harmful bacteria emit a red fluorescence. The device captures these red and green fluorescence signals in real time using specialized optical components to filter out the violet light, displaying the resultant image immediately on-screen. The MolecuLight i:X is precisely calibrated to detect fluorescent bacteria at levels higher than 104 CFU/g on a quantitative scale, or predominantly moderate to heavy growth on a semi-quantitative scale.
MolecuLight i:X illuminates the wound with a narrow band of violet light that causes endogenous fluorophores in the bacteria to fluoresce. Susceptible bacteria include Staphylocccus aureus and MRSA; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Escherichia coli; Coagulase-negative staphylococci; multiple Enterococcus species; multiple Proteus species; Klebsiella pneumonia; Beta-hemolytic streptococci (Group B); and multiple Enterobacter species. It is recommended that imaging be performed after surface blood has been removed from the wound bed and peri-wound areas.
“The MolecuLight i:X platform is a significant advancement in the management of chronic wounds that is already revolutionizing wound care practice in Canada and Europe,” said Ralph DaCosta, PhD, founder, director, and chief scientific officer of MolecuLight. “Thousands of patients have already experienced a change in their assessment and treatment by clinicians who feel empowered by the wound fluorescence images they are seeing.”
Related Links:
MolecuLight
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
- Deep Learning Model Accurately Diagnoses COPD Using Single Inhalation Lung CT Scan
- AI Model Reconstructs Sparse-View 3D CT Scan With Much Lower X-Ray Dose
- New Medical Scanner Identifies Brain Damage in Stroke Patients at Lower Magnetic Fields
Channels
Radiography
view channel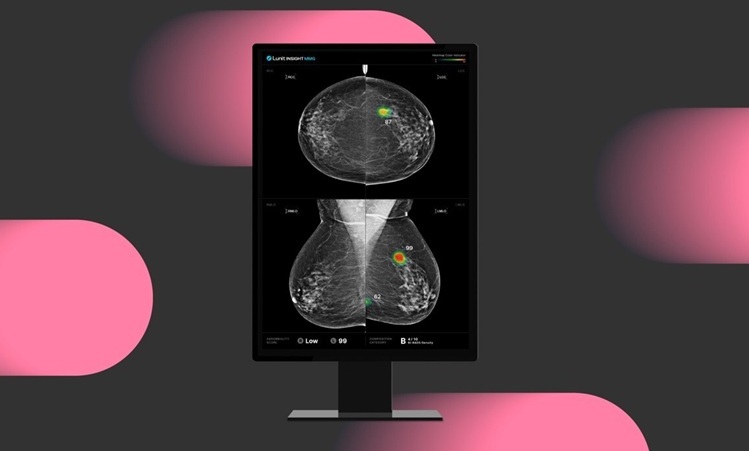
AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
A new study has revealed that an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solution significantly improves cancer detection in single-reader mammography settings without increasing recall rates, offering a... Read more
Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
For many years, healthcare professionals have depended on traditional 2D X-rays to diagnose common bone fractures, though small fractures or soft tissue damage, such as cancers, can often be missed.... Read moreMRI
view channel
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more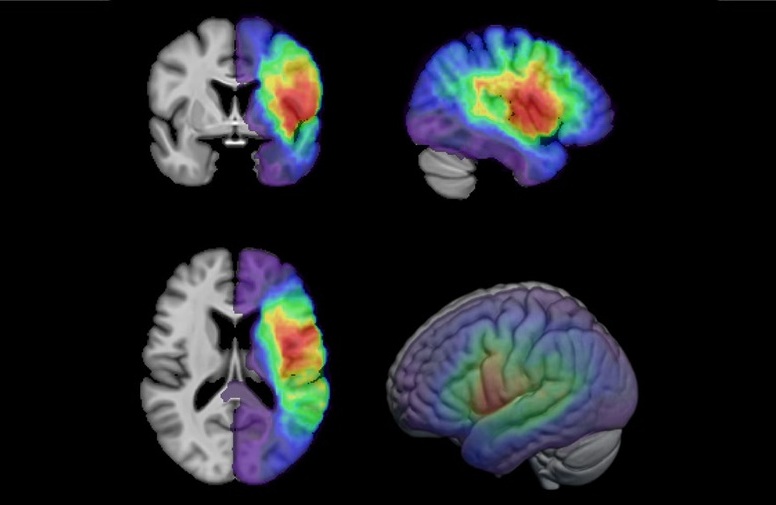
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel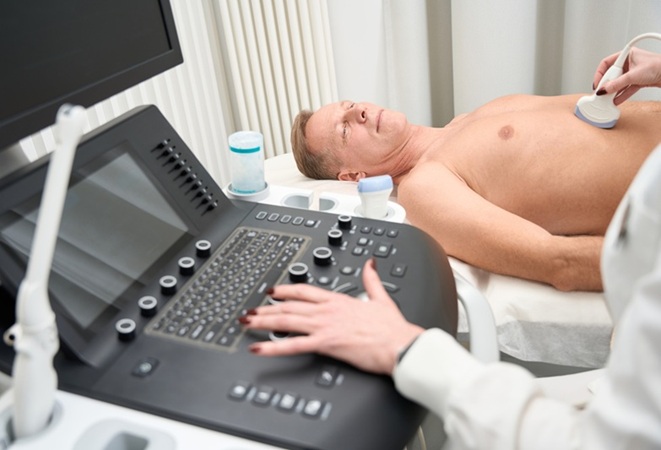
Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
Echocardiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses ultrasound to visualize the heart and its associated structures. This imaging test is commonly used as an early screening method when doctors suspect... Read more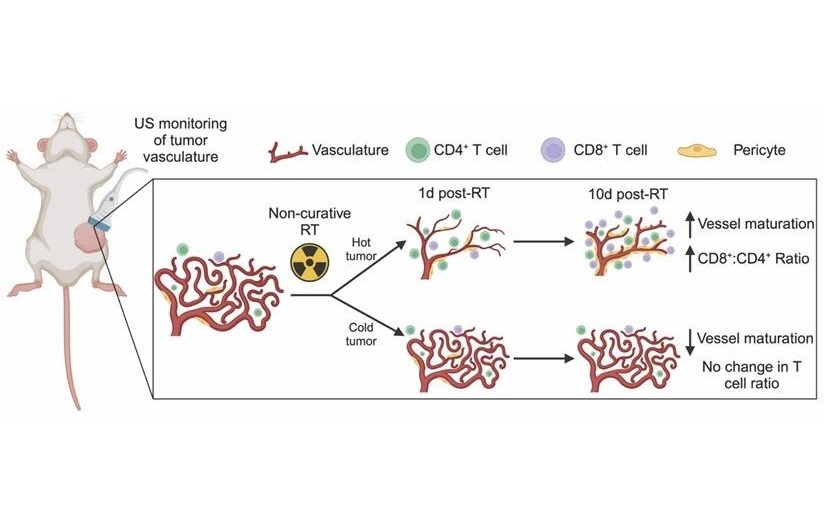
Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
While immunotherapy holds promise in the fight against triple-negative breast cancer, many patients fail to respond to current treatments. A major challenge has been predicting and monitoring how individual... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read more
Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease, are often diagnosed only after physical symptoms appear, by which time treatment may no longer be effective.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more














![Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242) Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242)](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-24/Brugarolas_F8.large.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpeg)