Machine Learning Shows Promise for Supporting Medical Decisions
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 01 Mar 2018 |
A number of studies presented at the 67th Annual Scientific Session of the American College of Cardiology (Washington, DC, USA) demonstrated how machine learning can be used to accurately predict clinical outcomes in patients with known or potential heart problems. The findings of these studies indicate that machine learning can usher in a new era in digital health care tools capable of enhancing healthcare delivery by aiding routine processes and helping physicians to assess the patients’ risk.
Clinical scoring systems and algorithms have been used in medical practice since a long time now, although there has recently been a visible increase in the application of machine learning to improve these tools. While traditional algorithms require all calculations to be pre-programmed, machine-learning algorithms deduce the optimal set of calculations by searching for patterns in large collections of patient data. New studies presented at ACC.18, which took place on March 10-12 in Orlando, USA, demonstrated how machine learning can be used to predict outcomes such as diagnosis, death or hospital readmission; improve upon standard risk assessment tools; elucidate factors that contribute to disease progression; or to advance personalized medicine by predicting a patient’s response to treatment.
For instance, in one study, researchers used machine learning to predict which patients would eventually be diagnosed with a heart attack after visiting a hospital emergency department for chest pain. Although chest pain is among the most common complaints in patients visiting the emergency department, only a fraction of such patients are ultimately diagnosed with a heart attack. In a pilot test, the algorithm was able to accurately predict a heart attack diagnosis 94% of the time in the validation data set. Researchers also ran the validation data through a standard clinical model (the hsTnT model, which incorporates only a patient’s age, sex and high-sensitivity troponin levels), which showed an accuracy of 88%. These results suggest that machine learning can offer a substantial improvement over current decision support tools.
“In a broad sense, machine-learning methods have been around for quite some time, but it’s just in the last few years that we have gained the large data sets and computational capabilities to use them for clinical applications,” said Daniel Lindholm, MD, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow at Uppsala University in Sweden and the study’s lead author. “I think that we will see more and more decision support systems based on machine learning. But even as machine learning can enhance medical practice, I do not think these algorithms will ultimately replace physicians but, rather, provide decision support based on the data at hand. Other things, such as empathy, human judgment and the patient-doctor relationship are crucial.”
Related Links:
American College of Cardiology
Clinical scoring systems and algorithms have been used in medical practice since a long time now, although there has recently been a visible increase in the application of machine learning to improve these tools. While traditional algorithms require all calculations to be pre-programmed, machine-learning algorithms deduce the optimal set of calculations by searching for patterns in large collections of patient data. New studies presented at ACC.18, which took place on March 10-12 in Orlando, USA, demonstrated how machine learning can be used to predict outcomes such as diagnosis, death or hospital readmission; improve upon standard risk assessment tools; elucidate factors that contribute to disease progression; or to advance personalized medicine by predicting a patient’s response to treatment.
For instance, in one study, researchers used machine learning to predict which patients would eventually be diagnosed with a heart attack after visiting a hospital emergency department for chest pain. Although chest pain is among the most common complaints in patients visiting the emergency department, only a fraction of such patients are ultimately diagnosed with a heart attack. In a pilot test, the algorithm was able to accurately predict a heart attack diagnosis 94% of the time in the validation data set. Researchers also ran the validation data through a standard clinical model (the hsTnT model, which incorporates only a patient’s age, sex and high-sensitivity troponin levels), which showed an accuracy of 88%. These results suggest that machine learning can offer a substantial improvement over current decision support tools.
“In a broad sense, machine-learning methods have been around for quite some time, but it’s just in the last few years that we have gained the large data sets and computational capabilities to use them for clinical applications,” said Daniel Lindholm, MD, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow at Uppsala University in Sweden and the study’s lead author. “I think that we will see more and more decision support systems based on machine learning. But even as machine learning can enhance medical practice, I do not think these algorithms will ultimately replace physicians but, rather, provide decision support based on the data at hand. Other things, such as empathy, human judgment and the patient-doctor relationship are crucial.”
Related Links:
American College of Cardiology
Latest Business News
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
Breast cancer represents 15.5% of new cancer cases and 7% of cancer-related deaths in the United States. Approximately 13.1% of women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lifetime.... Read more
Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
Mammography screening helps reduce breast cancer mortality; however, its accuracy is not perfect. For decades, various strategies have been employed to enhance the interpretive performance of mammography,... Read more (1).jpg)
AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Detects Pulmonary Nodules Three Years Before Lung Cancer Symptoms
Lung cancer has one of the worst survival rates among all cancers, with more than two-thirds of patients diagnosed at an advanced stage, making curative treatment no longer viable. The issue of missed... Read moreMRI
view channel
Groundbreaking AI-Powered Software Significantly Enhances Brain MRI
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) utilizes contrast agents to illuminate specific tissues or abnormalities, leading to improved visualization and more comprehensive information.... Read more.jpeg)
MRI Predicts Patient Outcomes and Tumor Recurrence in Rectal Cancer Patients
Colorectal cancer is on the rise among younger adults—those under 50—while it has been declining in older populations. It is estimated that approximately 1 in 23 men and 1 in 25 women will be diagnosed... Read more
Portable MRI System Dramatically Cuts Time-To-Scan vs. Conventional MRI in Stroke Patients
Imaging of the brain is crucial for the management of acute stroke and transient ischemic attack. Key roles of imaging include confirming the diagnosis, determining treatment eligibility, indicating the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Ultrasound Can Identify Sources of Brain-Related Issues and Disorders Before Treatment
For many years, healthcare professionals worldwide have relied on ultrasound to monitor the growth of unborn infants and evaluate the health of internal organs. However, ultrasound technology, once primarily... Read more
New Guideline on Handling Endobronchial Ultrasound Transbronchial Needle Samples
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) has become the standard procedure for the initial diagnosis and staging of lung cancer; however, there is limited guidance on... Read more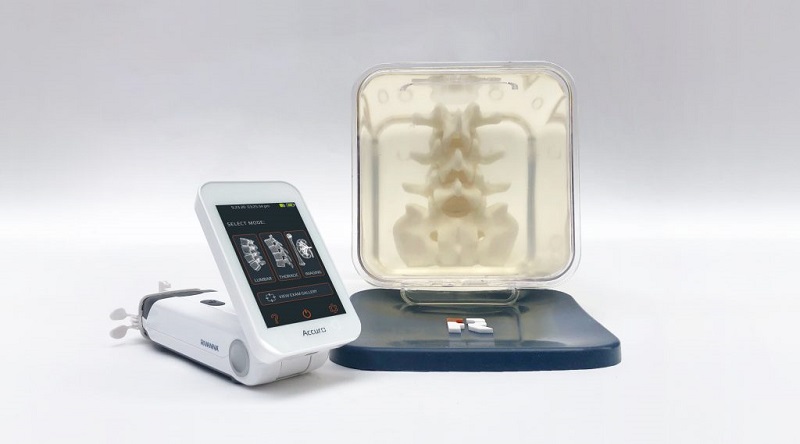
Groundbreaking Ultrasound-Guided Needle Insertion System Improves Medical Procedures
Ultrasound-guided neuraxial procedures have traditionally been hampered by technical challenges, such as the need for three hands to manage the needle, probe, and syringe simultaneously, steep needle angles... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Software Enhances Diagnosis and Monitoring of Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is marked by the buildup of beta-amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles in the brain. These deposits of beta-amyloid and tau appear in various brain regions at differing rates as the brain ages.... Read more.jpg)
New Photon-Counting CT Technique Diagnoses Osteoarthritis Before Symptoms Develop
X-ray imaging has evolved significantly since its introduction in 1895. This technique is known for capturing images quickly, making it ideal for emergency situations; however, it does not provide adequate... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
Low-Dose CT Screening for Lung Cancer Can Benefit Heavy Smokers
Lung cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage, with only about one-fifth to one-sixth of patients surviving five years after diagnosis. A new report now suggests that low-dose computed tomography (CT)... Read more![Image: A kidney showing positive [89Zr]Zr-girentuximab PET and histologically confirmed clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (Photo courtesy of Dr. Brian Shuch/UCLA Health) Image: A kidney showing positive [89Zr]Zr-girentuximab PET and histologically confirmed clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (Photo courtesy of Dr. Brian Shuch/UCLA Health)](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2024-10-04/ca9scan.jpg)
Non-Invasive Imaging Technique Accurately Detects Aggressive Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancers, known as renal cell carcinomas, account for 90% of solid kidney tumors, with over 81,000 new cases diagnosed annually in the United States. Among the various types, clear-cell renal cell... Read more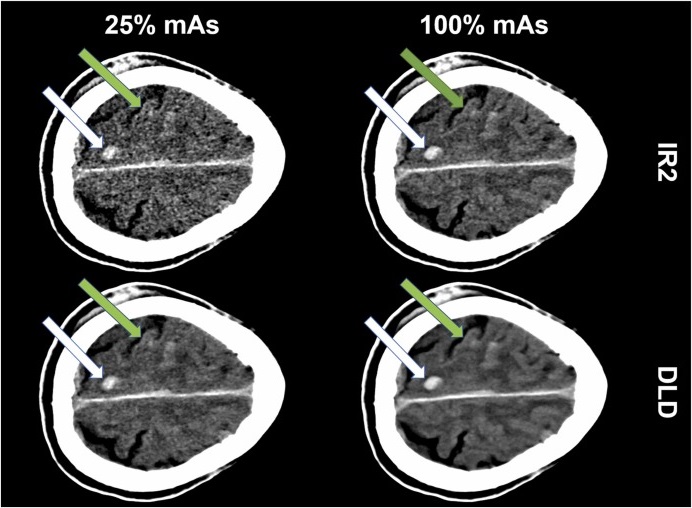
AI Algorithm Reduces Unnecessary Radiation Exposure in Traumatic Neuroradiological CT Scans
Traumatic neuroradiological emergencies encompass conditions that require immediate and accurate diagnosis for effective treatment and optimal patient outcomes. These emergencies can include injuries to... Read more
New Solution Enhances AI-Based Quality Control and Diagnosis in Medical Imaging
Medical image data makes up 80% of clinical data, and artificial intelligence (AI) offers significant potential to unlock its full value, which is crucial for clinical diagnosis, decision-making, and disease... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel.jpeg)
Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
A stroke is typically an acute incident primarily caused by a blockage in a brain blood vessel, which disrupts the adequate blood supply to brain tissue and results in the permanent loss of brain cells.... Read more
Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
A new global partnership aims to explore opportunities to further expand access to advanced pre-and post-operative imaging technologies for spine care. Medtronic plc (Galway, Ireland) and Siemens Healthineers... Read more
RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA, Oak Brook, IL, USA) has announced highlights of the Technical Exhibits at RSNA 2024: Building Intelligent Connections, the Society’s 110th Scientific Assembly... Read more













.jpg)