New Metal-free Contrast Agent May Be Safer for Patients
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 25 Jul 2017 |
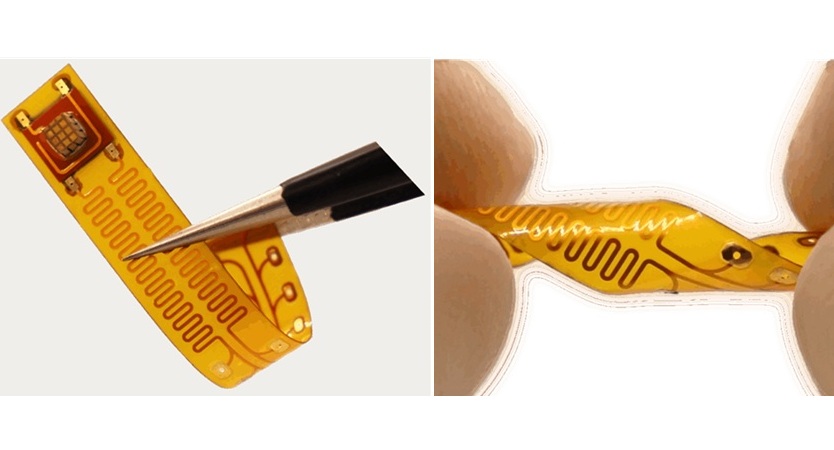
Image: Researchers have developed a safer hydroxide organic MRI contrast agent, as an alternative to metal based ones, for young children and other high-risk patients (Photo courtesy of MIT / University of Nebraska).
Researchers have developed a new metal-free MRI contrast agent that could be used for high-risk patient groups and make longer-term tumor imaging more feasible.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) tumor imaging scans are often used together with intravenous contrast agents, most commonly gadolinium-based ones. These agents contain metal compounds that can be harmful for patients with kidney problems, and for young children.
Now researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT; Boston, MA, USA), and the University of Nebraska (Lincoln, NB, USA) have developed an organic nitroxide-based metal-free contrast agent that is safer for these high-risk groups. The new agent also accumulates for longer at a tumor site providing more data for MRI scans.
The researchers loaded the nitroxide agent into a spherical Brush-Arm Star Polymer (BASP) structure with a hydrophilic core and a hydrophobic shell. They also found that they could substantially increase the MRI relaxivity of the agent, to around the level of metal-based agents. The BASP shell protects the radicals in the bloodstream allowing them to survive for up to 20 hours.
The new contrast agent could also be modified to carry drugs, in addition to the MRI contrast agent, and allow for long-term imaging and follow-up treatments to monitor whether the drug is able to shrink the tumor. Another possibility under investigation is combining the contrast agent particles with antibodies that can target specific cells.
Senior author of the study, associate professor of Chemistry at MIT, Jeremiah Johnson, said, “This is an entirely organic, metal-free MRI contrast agent that would allow cancer researchers to start to think about how to image tumors in a dynamic way over long periods of time.
Related Links:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
University of Nebraska
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) tumor imaging scans are often used together with intravenous contrast agents, most commonly gadolinium-based ones. These agents contain metal compounds that can be harmful for patients with kidney problems, and for young children.
Now researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT; Boston, MA, USA), and the University of Nebraska (Lincoln, NB, USA) have developed an organic nitroxide-based metal-free contrast agent that is safer for these high-risk groups. The new agent also accumulates for longer at a tumor site providing more data for MRI scans.
The researchers loaded the nitroxide agent into a spherical Brush-Arm Star Polymer (BASP) structure with a hydrophilic core and a hydrophobic shell. They also found that they could substantially increase the MRI relaxivity of the agent, to around the level of metal-based agents. The BASP shell protects the radicals in the bloodstream allowing them to survive for up to 20 hours.
The new contrast agent could also be modified to carry drugs, in addition to the MRI contrast agent, and allow for long-term imaging and follow-up treatments to monitor whether the drug is able to shrink the tumor. Another possibility under investigation is combining the contrast agent particles with antibodies that can target specific cells.
Senior author of the study, associate professor of Chemistry at MIT, Jeremiah Johnson, said, “This is an entirely organic, metal-free MRI contrast agent that would allow cancer researchers to start to think about how to image tumors in a dynamic way over long periods of time.
Related Links:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
University of Nebraska
Latest MRI News
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
Breast cancer screening programs rely heavily on radiologists interpreting mammograms, a process that is time-intensive and subject to errors. While artificial intelligence (AI) models have shown strong... Read more
AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
Breast cancer remains one of the most common cancers among women, with about one in eight receiving a diagnosis in their lifetime. Despite widespread use of mammography, about 34% of patients in the U.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel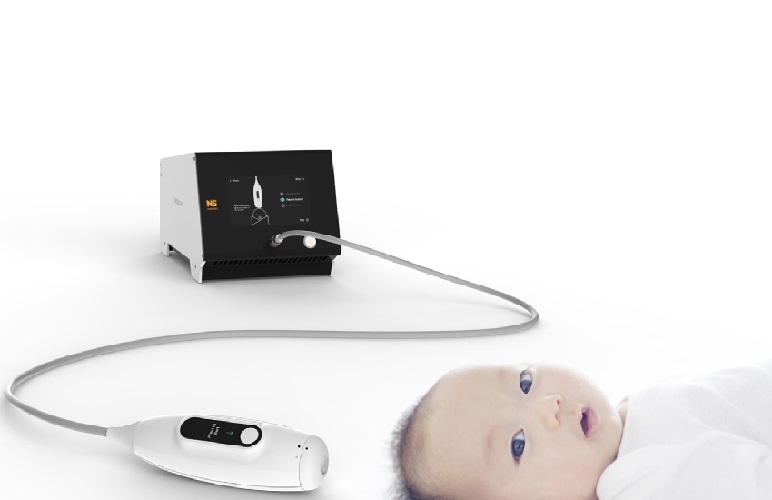
Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
Meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can be fatal in infants if not diagnosed and treated early. Even when treated, it may leave lasting damage, such as cognitive... Read more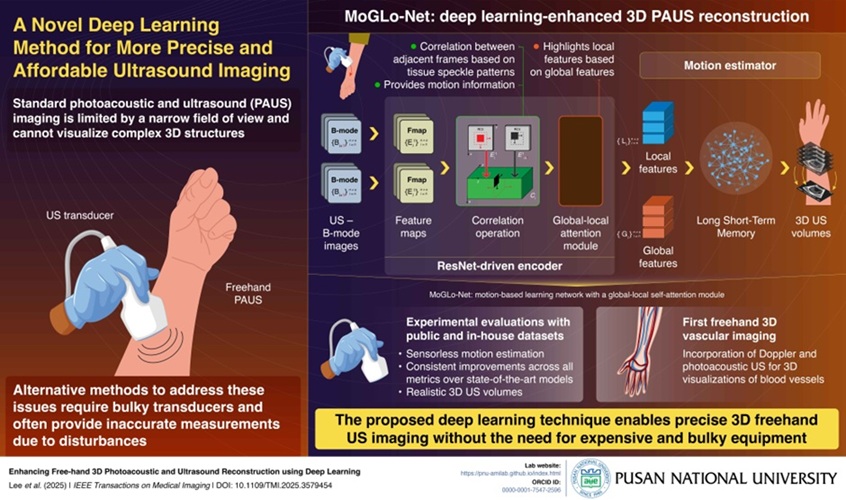
Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is a vital diagnostic technique used to visualize internal organs and tissues in real time and to guide procedures such as biopsies and injections. When paired with photoacoustic imaging... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel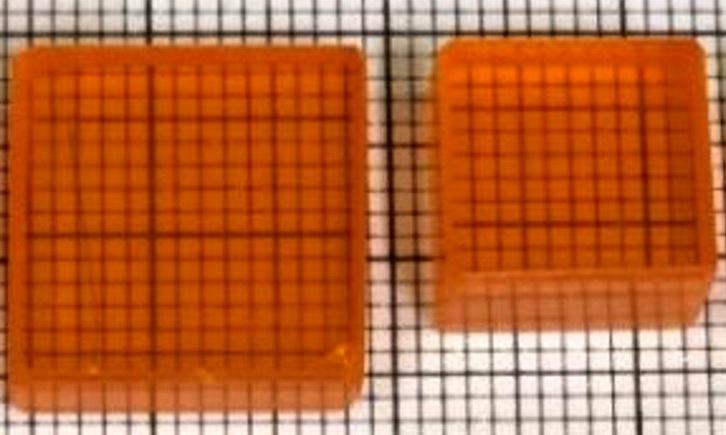
New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
Nuclear medicine scans like single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) allow doctors to observe heart function, track blood flow, and detect hidden diseases. However, current detectors are either... Read more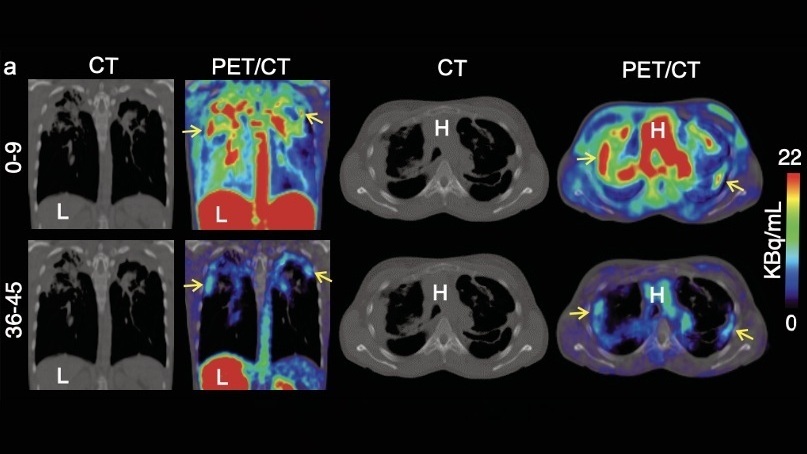
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
In pancreatic cancer, detecting whether the disease has spread to other organs is critical for determining whether surgery is appropriate. If metastasis is present, surgery is not recommended, yet current... Read more
Cutting-Edge Angio-CT Solution Offers New Therapeutic Possibilities
Maintaining accuracy and safety in interventional radiology is a constant challenge, especially as complex procedures require both high precision and efficiency. Traditional setups often involve multiple... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more