Intraoperative Holographics Support Cardiac Procedures
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 08 Oct 2019 |
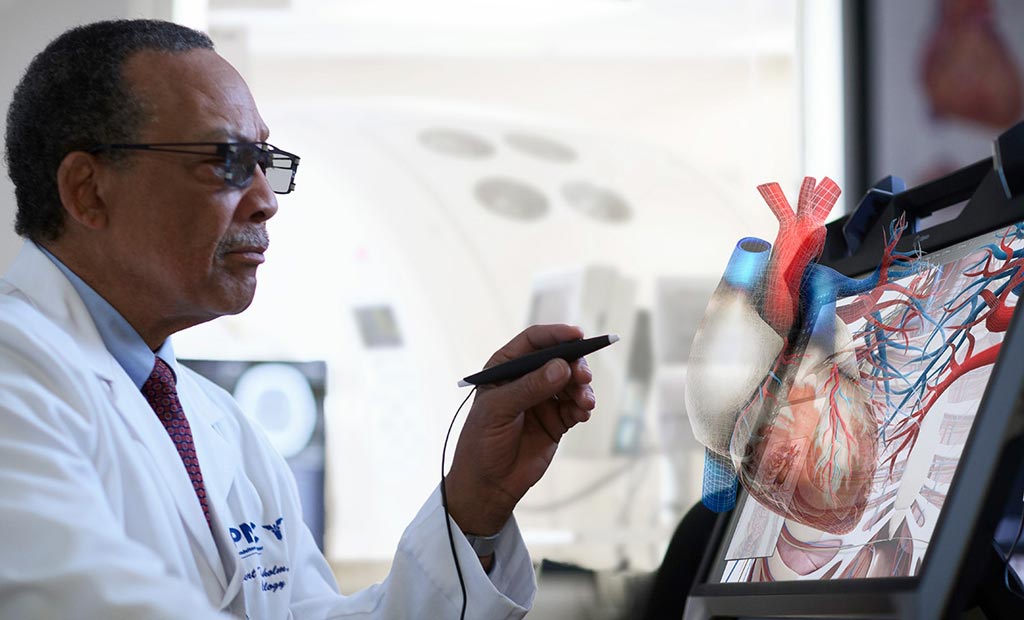
Image: VR glasses and an electronic scribe help manipulate a holographic heart (Photo courtesy of EchoPixel).
A novel intraoperative software suite provides naked-eye, touchless, and interactive three-dimensional (3D) anatomical imaging to enhance structural heart procedures.
The EchoPixel (Santa Clara, CA, USA) True3D anatomical imaging tools are designed to provide clinicians with a holographic experience by using special virtual reality (VR) glasses that help them visualize and interact with patient-specific organs and tissue, just as they would with physical objects in the real world. This allows for enhanced pre-operative planning, improved patient selection, increased patient engagement, and the completion of increasingly complex structural heart and congenital heart disease procedures in both adults and pediatric patients in shorter timeframes.
The interactive VR software leverages computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), C-Arm fluoroscopy images, and echocardiography to create life-size holographic versions of organs, blood vessels, and other structures. This allows physicians to interact with a digital twin of the patient specific anatomy to identify optimal treatment target, approach, and catheter position, capture accurate measurements, distances, and angles, and virtually try in and fit implants and cardiac devices. The enhanced visualization of anatomical structures and spatial relationships also facilitate completion of procedures with reproducible, reliable outcomes.
“Building on the success of our existing technology in pediatric congenital heart procedures, EchoPixel is committed to enabling digital surgery, providing and continuously improving transformative technology designed to help clinicians improve and personalize delivery of minimally invasive therapies,” said Sergio Aguirre, CEO of EchoPixel. “Going forward, our vision for the OR of the future involves expanding our mixed reality True3D software platform to integrate AI and robotics to enable the completion of more precise and personalized procedures.”
“EchoPixel's technology lets you effortlessly interact with 3D images to better understand complex cardiac anatomy and the anatomic variability that is commonly seen in structural heart disease patients,” said Saurabh Sanon, MD, of Florida Atlantic University (Boca Raton, USA). “We are currently working on a research study comparing procedure times with and without the technology, and the initial results are promising in terms of reducing procedure times and device waste.”
In order to successfully identify an area of interest from a 3D medical data set, as those produced by CT, MRI and other devices, doctors are required to mentally integrate a series of 2D images and cognitively extract the relevant relationships that define the tissue or organ of interest, as well as its neighboring anatomy. In complex cases, they must visually map multiple views of the same data to find appropriate correspondences of one view with another view to produce a match, and determine if what they see is the tissue they want to evaluate.
Related Links:
EchoPixel
Florida Atlantic University
The EchoPixel (Santa Clara, CA, USA) True3D anatomical imaging tools are designed to provide clinicians with a holographic experience by using special virtual reality (VR) glasses that help them visualize and interact with patient-specific organs and tissue, just as they would with physical objects in the real world. This allows for enhanced pre-operative planning, improved patient selection, increased patient engagement, and the completion of increasingly complex structural heart and congenital heart disease procedures in both adults and pediatric patients in shorter timeframes.
The interactive VR software leverages computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), C-Arm fluoroscopy images, and echocardiography to create life-size holographic versions of organs, blood vessels, and other structures. This allows physicians to interact with a digital twin of the patient specific anatomy to identify optimal treatment target, approach, and catheter position, capture accurate measurements, distances, and angles, and virtually try in and fit implants and cardiac devices. The enhanced visualization of anatomical structures and spatial relationships also facilitate completion of procedures with reproducible, reliable outcomes.
“Building on the success of our existing technology in pediatric congenital heart procedures, EchoPixel is committed to enabling digital surgery, providing and continuously improving transformative technology designed to help clinicians improve and personalize delivery of minimally invasive therapies,” said Sergio Aguirre, CEO of EchoPixel. “Going forward, our vision for the OR of the future involves expanding our mixed reality True3D software platform to integrate AI and robotics to enable the completion of more precise and personalized procedures.”
“EchoPixel's technology lets you effortlessly interact with 3D images to better understand complex cardiac anatomy and the anatomic variability that is commonly seen in structural heart disease patients,” said Saurabh Sanon, MD, of Florida Atlantic University (Boca Raton, USA). “We are currently working on a research study comparing procedure times with and without the technology, and the initial results are promising in terms of reducing procedure times and device waste.”
In order to successfully identify an area of interest from a 3D medical data set, as those produced by CT, MRI and other devices, doctors are required to mentally integrate a series of 2D images and cognitively extract the relevant relationships that define the tissue or organ of interest, as well as its neighboring anatomy. In complex cases, they must visually map multiple views of the same data to find appropriate correspondences of one view with another view to produce a match, and determine if what they see is the tissue they want to evaluate.
Related Links:
EchoPixel
Florida Atlantic University
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
- Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
- CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
- Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
- CT-Based Deep Learning Algorithm Accurately Differentiates Benign From Malignant Vertebral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Could Help Patients Avoid Thyroid Surgery
- Self-Driving Mobile C-Arm Reduces Imaging Time during Surgery
- AR Application Turns Medical Scans Into Holograms for Assistance in Surgical Planning
- Imaging Technology Provides Ground-Breaking New Approach for Diagnosing and Treating Bowel Cancer
- CT Coronary Calcium Scoring Predicts Heart Attacks and Strokes
- AI Model Detects 90% of Lymphatic Cancer Cases from PET and CT Images
- Breakthrough Technology Revolutionizes Breast Imaging
- State-Of-The-Art System Enhances Accuracy of Image-Guided Diagnostic and Interventional Procedures
- Catheter-Based Device with New Cardiovascular Imaging Approach Offers Unprecedented View of Dangerous Plaques
- AI Model Draws Maps to Accurately Identify Tumors and Diseases in Medical Images
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more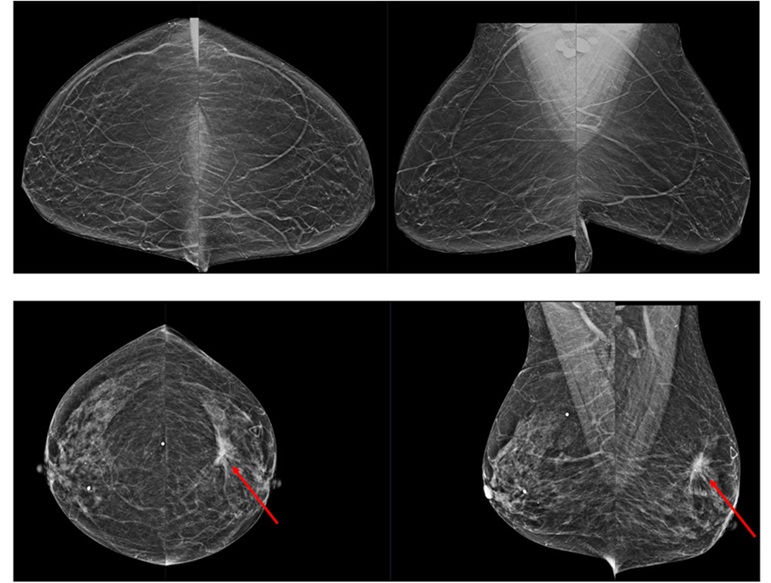
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel
World's First Sensor Detects Errors in MRI Scans Using Laser Light and Gas
MRI scanners are daily tools for doctors and healthcare professionals, providing unparalleled 3D imaging of the brain, vital organs, and soft tissues, far surpassing other imaging technologies in quality.... Read more
Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
Gadolinium, a heavy metal used for over three decades as a contrast agent in medical imaging, enhances the clarity of MRI scans by highlighting affected areas. Despite its utility, gadolinium not only... Read more.jpg)
Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
Prostate cancer is a leading health concern globally, consistently being one of the most common types of cancer among men and a major cause of cancer-related deaths. In the United States, it is the most... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Largest Model Trained On Echocardiography Images Assesses Heart Structure and Function
Foundation models represent an exciting frontier in generative artificial intelligence (AI), yet many lack the specialized medical data needed to make them applicable in healthcare settings.... Read more.jpg)
Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
The current standard of care of using angiographic information is often inadequate for accurately assessing vessel size in the estimated 20 million people in the U.S. who suffer from peripheral vascular disease.... Read more
Deep Learning Advances Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound localization microscopy (ULM) is an advanced imaging technique that offers high-resolution visualization of microvascular structures. It employs microbubbles, FDA-approved contrast agents, injected... Read more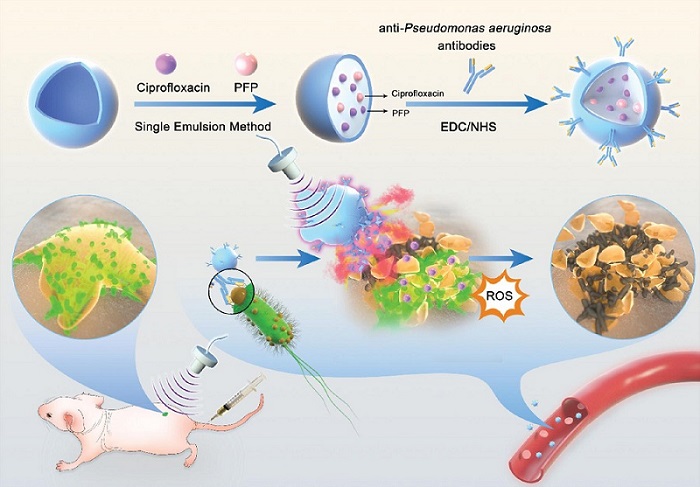
Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
Biofilms, formed by bacteria aggregating into dense communities for protection against harsh environmental conditions, are a significant contributor to various infectious diseases. Biofilms frequently... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more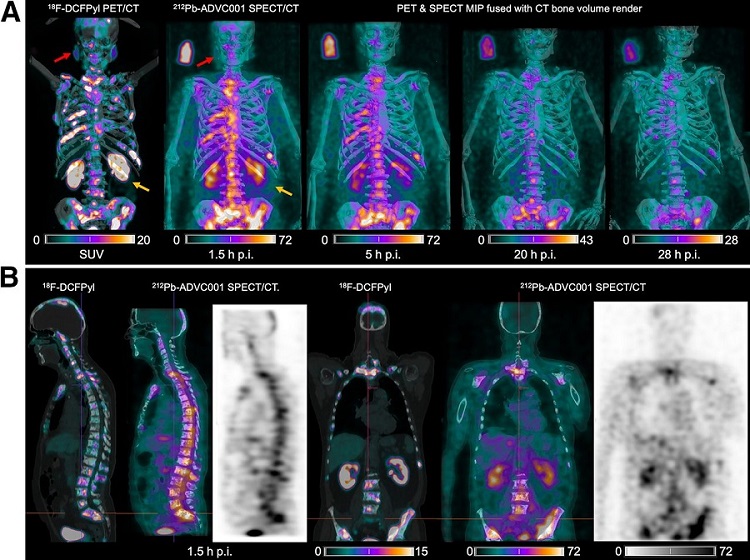
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreNew Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer, with less than a 30% five-year survival rate for those diagnosed in late stages. Despite surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy being the standard... Read more
AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
Cardiac amyloidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal protein deposits (amyloids) in the heart muscle, severely affects heart function and can lead to heart failure or death without... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
A key challenge for clinicians treating patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) is that after a certain amount of time, they continue to worsen even though their MRIs show no change. A new study has now... Read more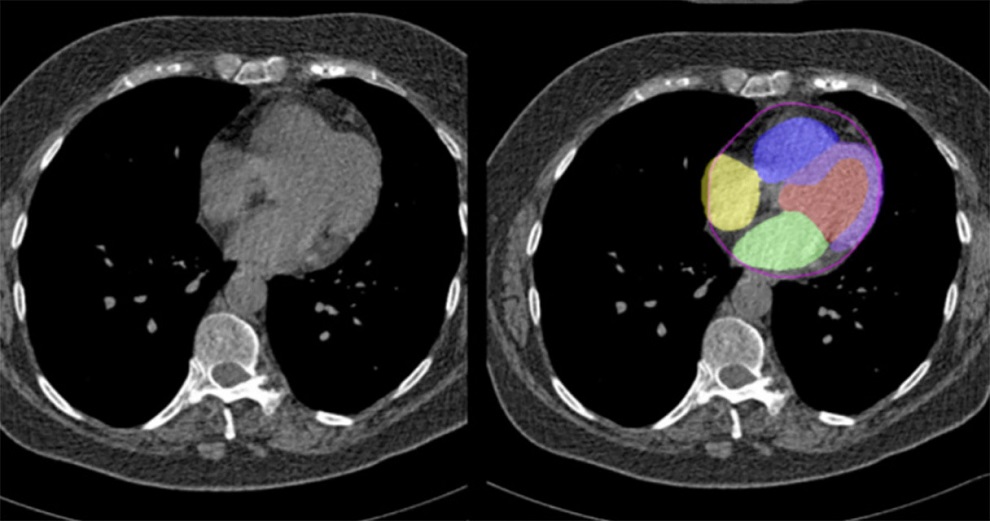
Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
Chest computed tomography (CT) is a common diagnostic tool, with approximately 15 million scans conducted each year in the United States, though many are underutilized or not fully explored.... Read more
New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
In the field of biomedicine, segmentation is the process of annotating pixels from an important structure in medical images, such as organs or cells. Artificial Intelligence (AI) models are utilized to... Read more.jpg)
CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), one of the leading causes of death worldwide, involves the narrowing of coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis, resulting in insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more