Novel Intraoperative Probe Developed for Cancer Surgery
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 03 Jul 2017 |
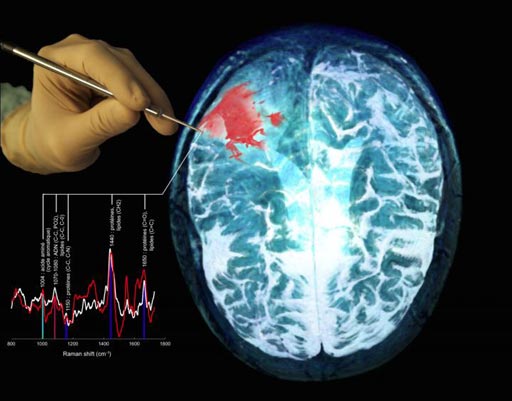
Image: A depiction of the new multimodal probe in use during surgery, together with a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan of a brain cancer patient, showing the tumor in red (Photo courtesy of Frédéric Leblond and Kevin Petrecca).
An innovative intraoperative probe for detecting different types of tumor cells has been developed by researchers in Canada.
The multimodal hand-held Raman optical spectroscopy probe enables surgeons to detect nearly all cancer cells during brain surgery.
The scientists from the Polytechnique Montréal (Montréal, Canada), and two other hospitals and Universities developed the hand-held Raman spectroscopy probe. The device is now accurate, sensitive and specific enough for detecting brain, colon, lung, and skin cancer cells. During intraoperative testing the probe showed nearly 100% sensitivity for detecting cancer cells. Details of the breakthrough technology were published in the June 28, 2017, issue of the American Association for Cancer Research journal Cancer Research.
The unique feature of the new second-generation system is that it can be used in real-time, during a surgical procedure, to detect cancer cells. The multimodal probe uses intrinsic fluorescence spectroscopy, and diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy technologies. A randomized clinical trial is currently under way using the first-generation Raman spectroscopy probe for patients with gliomas, and will help researchers develop a protocol for a clinical trial of the new second-generation multimodal probe.
Chief of Neurosurgery, brain cancer researcher Dr. Petrecca, said, "Minimizing, or completely eliminating, the number of cancer cells during surgery is a critical part of cancer treatment, yet detecting cancer cells during surgery is challenging. Often it is impossible to visually distinguish cancer from normal brain, so invasive brain cancer cells frequently remain after surgery, leading to cancer recurrence and a worse prognosis. Surgically minimizing the number of cancer cells improves patient outcomes. A technology with extremely high accuracy is necessary, since surgeons will be using this information to help determine if tissues contain cancer cells or not."
Related Links:
Polytechnique Montréal
The multimodal hand-held Raman optical spectroscopy probe enables surgeons to detect nearly all cancer cells during brain surgery.
The scientists from the Polytechnique Montréal (Montréal, Canada), and two other hospitals and Universities developed the hand-held Raman spectroscopy probe. The device is now accurate, sensitive and specific enough for detecting brain, colon, lung, and skin cancer cells. During intraoperative testing the probe showed nearly 100% sensitivity for detecting cancer cells. Details of the breakthrough technology were published in the June 28, 2017, issue of the American Association for Cancer Research journal Cancer Research.
The unique feature of the new second-generation system is that it can be used in real-time, during a surgical procedure, to detect cancer cells. The multimodal probe uses intrinsic fluorescence spectroscopy, and diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy technologies. A randomized clinical trial is currently under way using the first-generation Raman spectroscopy probe for patients with gliomas, and will help researchers develop a protocol for a clinical trial of the new second-generation multimodal probe.
Chief of Neurosurgery, brain cancer researcher Dr. Petrecca, said, "Minimizing, or completely eliminating, the number of cancer cells during surgery is a critical part of cancer treatment, yet detecting cancer cells during surgery is challenging. Often it is impossible to visually distinguish cancer from normal brain, so invasive brain cancer cells frequently remain after surgery, leading to cancer recurrence and a worse prognosis. Surgically minimizing the number of cancer cells improves patient outcomes. A technology with extremely high accuracy is necessary, since surgeons will be using this information to help determine if tissues contain cancer cells or not."
Related Links:
Polytechnique Montréal
Latest MRI News
- Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
- World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
- World's First Sensor Detects Errors in MRI Scans Using Laser Light and Gas
- Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
- Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
- PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
- Two-Part MRI Scan Detects Prostate Cancer More Quickly without Compromising Diagnostic Quality
- World’s Most Powerful MRI Machine Images Living Brain with Unrivaled Clarity
- New Whole-Body Imaging Technology Makes It Possible to View Inflammation on MRI Scan
- Combining Prostate MRI with Blood Test Can Avoid Unnecessary Prostate Biopsies
- New Treatment Combines MRI and Ultrasound to Control Prostate Cancer without Serious Side Effects
- MRI Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer
- Combined PET-MRI Scan Improves Treatment for Early Breast Cancer Patients
- 4D MRI Could Improve Clinical Assessment of Heart Blood Flow Abnormalities
- MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound Therapy Shows Promise in Treating Prostate Cancer
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel
Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has significantly transformed healthcare, providing a noninvasive, radiation-free method for detailed imaging. It is especially promising for the future of medical diagnosis... Read more
World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
The world's first whole-body ultra-high field (UHF) MRI has officially come to market, marking a remarkable advancement in diagnostic radiology. United Imaging (Shanghai, China) has secured clearance from the U.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Diagnostic System Automatically Analyzes TTE Images to Identify Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most prevalent congenital anomalies worldwide, presenting substantial health and financial challenges for affected patients. Early detection and treatment of... Read more
Super-Resolution Imaging Technique Could Improve Evaluation of Cardiac Conditions
The heart depends on efficient blood circulation to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and waste. Yet, when heart vessels are damaged, it can disrupt... Read more
First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity
Ultrasound scans are essential for identifying and diagnosing various medical conditions, but often, patients must wait weeks or months for results due to a shortage of qualified medical professionals... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channelNew PET Agent Rapidly and Accurately Visualizes Lesions in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) represents 70-80% of renal cell carcinoma cases. While localized disease can be effectively treated with surgery and ablative therapies, one-third of patients either... Read more
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more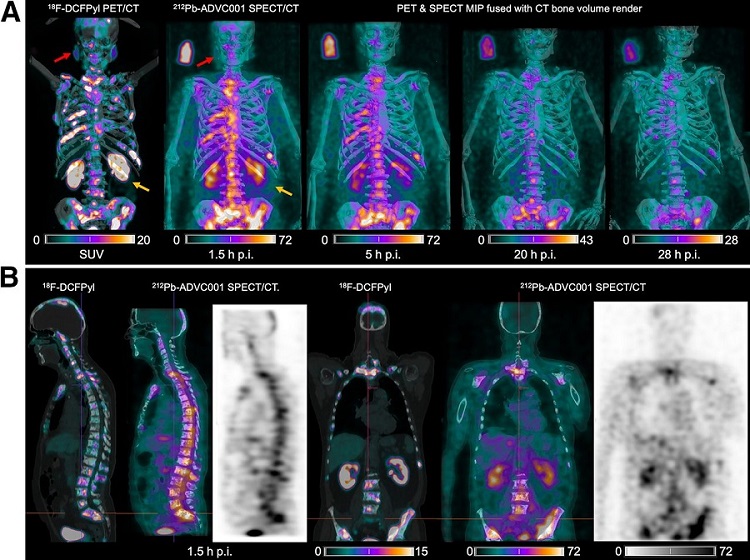
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Hologic, Inc. (Marlborough, MA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Endomagnetics Ltd. (Cambridge, UK), a privately held developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately... Read more
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more