Cause of Blurry Vision on Long Space Missions Found
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Jan 2017 |
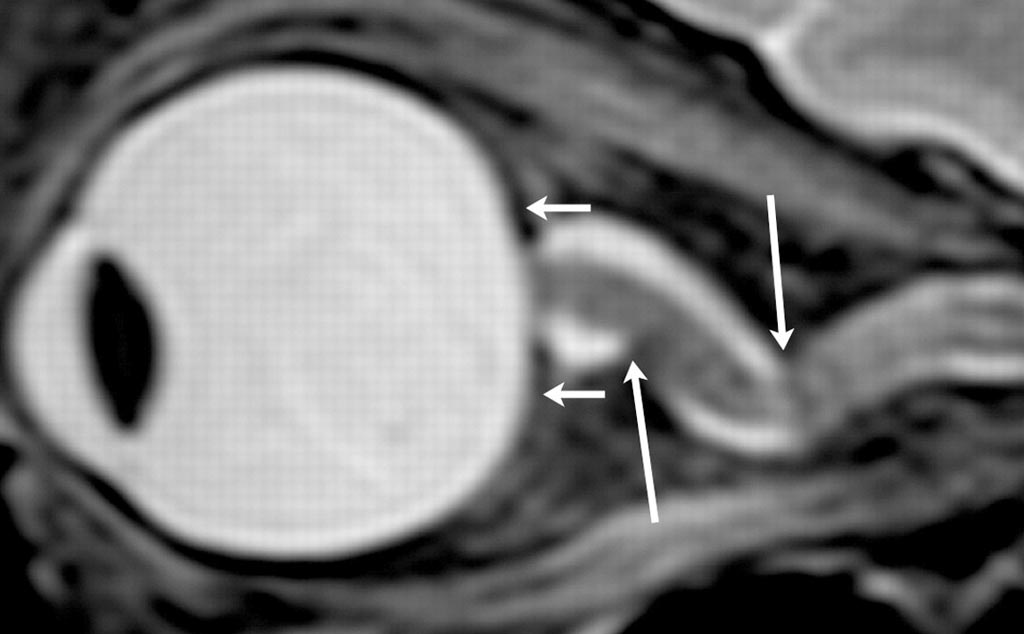
Image: An abruptly angulated foci in the optic nerve sheath, as well as globe flattening at the back of the eyeball, from a 2012 study of astronauts (Photo courtesy of RSNA).
Scientists studying the cause of visual impairments suffered by astronauts during long space missions have discovered that the problem is related to changes in the volume of Cerebro-Spinal Fluid (CSF), flattening of the eyeballs, and increased protrusion of the optic nerves.
The researchers carried out high-resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans of the eye orbits and the brains of seven astronauts before and shortly after long-duration missions on the International Space Station (ISS). The researchers compared the results with those of astronauts from nine short-duration missions in space. The MRI results were analyzed using advanced quantitative imaging algorithms.
Flight surgeons and scientists at the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) had already observed for ten years that nearly two-thirds of astronauts on long ISS missions suffered from Visual Impairment Intracranial Pressure (VIIP).
The results showed significantly increased post-flight flattening of the eyeballs and increased CSF volume in astronauts on long-duration flights compared to those on short-duration flights. Brain grey or white matter volume was not significantly different between the groups.
Lead author of the study, Noam Alperin, PhD, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, said, "People initially didn't know what to make of it, and by 2010 there was growing concern as it became apparent that some of the astronauts had severe structural changes that were not fully reversible upon return to earth. On earth, the CSF system is built to accommodate these pressure changes, but in space the system is confused by the lack of the posture-related pressure changes. If the ocular structural deformations are not identified early, astronauts could suffer irreversible damage. As the eye globe becomes more flattened, the astronauts become hyperopic, or far-sighted."
The researchers carried out high-resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans of the eye orbits and the brains of seven astronauts before and shortly after long-duration missions on the International Space Station (ISS). The researchers compared the results with those of astronauts from nine short-duration missions in space. The MRI results were analyzed using advanced quantitative imaging algorithms.
Flight surgeons and scientists at the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) had already observed for ten years that nearly two-thirds of astronauts on long ISS missions suffered from Visual Impairment Intracranial Pressure (VIIP).
The results showed significantly increased post-flight flattening of the eyeballs and increased CSF volume in astronauts on long-duration flights compared to those on short-duration flights. Brain grey or white matter volume was not significantly different between the groups.
Lead author of the study, Noam Alperin, PhD, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, said, "People initially didn't know what to make of it, and by 2010 there was growing concern as it became apparent that some of the astronauts had severe structural changes that were not fully reversible upon return to earth. On earth, the CSF system is built to accommodate these pressure changes, but in space the system is confused by the lack of the posture-related pressure changes. If the ocular structural deformations are not identified early, astronauts could suffer irreversible damage. As the eye globe becomes more flattened, the astronauts become hyperopic, or far-sighted."
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- Bone Density Test Uses Existing CT Images to Predict Fractures
- AI Predicts Cardiac Risk and Mortality from Routine Chest CT Scans
- Radiation Therapy Computed Tomography Solution Boosts Imaging Accuracy
- PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
- Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
- CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
- Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
- CT-Based Deep Learning Algorithm Accurately Differentiates Benign From Malignant Vertebral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Could Help Patients Avoid Thyroid Surgery
- Self-Driving Mobile C-Arm Reduces Imaging Time during Surgery
- AR Application Turns Medical Scans Into Holograms for Assistance in Surgical Planning
- Imaging Technology Provides Ground-Breaking New Approach for Diagnosing and Treating Bowel Cancer
- CT Coronary Calcium Scoring Predicts Heart Attacks and Strokes
- AI Model Detects 90% of Lymphatic Cancer Cases from PET and CT Images
- Breakthrough Technology Revolutionizes Breast Imaging
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel
Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has significantly transformed healthcare, providing a noninvasive, radiation-free method for detailed imaging. It is especially promising for the future of medical diagnosis... Read more
World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
The world's first whole-body ultra-high field (UHF) MRI has officially come to market, marking a remarkable advancement in diagnostic radiology. United Imaging (Shanghai, China) has secured clearance from the U.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Diagnostic System Automatically Analyzes TTE Images to Identify Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most prevalent congenital anomalies worldwide, presenting substantial health and financial challenges for affected patients. Early detection and treatment of... Read more
Super-Resolution Imaging Technique Could Improve Evaluation of Cardiac Conditions
The heart depends on efficient blood circulation to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and waste. Yet, when heart vessels are damaged, it can disrupt... Read more
First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity
Ultrasound scans are essential for identifying and diagnosing various medical conditions, but often, patients must wait weeks or months for results due to a shortage of qualified medical professionals... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New PET Biomarker Predicts Success of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy
Immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), have shown promising clinical results in treating melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other tumor types. However, the effectiveness of these... Read moreNew PET Agent Rapidly and Accurately Visualizes Lesions in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) represents 70-80% of renal cell carcinoma cases. While localized disease can be effectively treated with surgery and ablative therapies, one-third of patients either... Read more
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more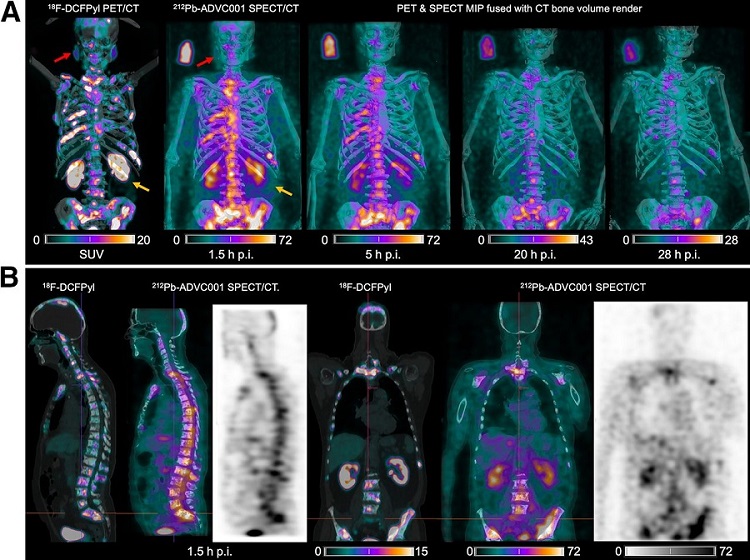
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Hologic, Inc. (Marlborough, MA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Endomagnetics Ltd. (Cambridge, UK), a privately held developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately... Read more
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more