AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 20 Feb 2025 |
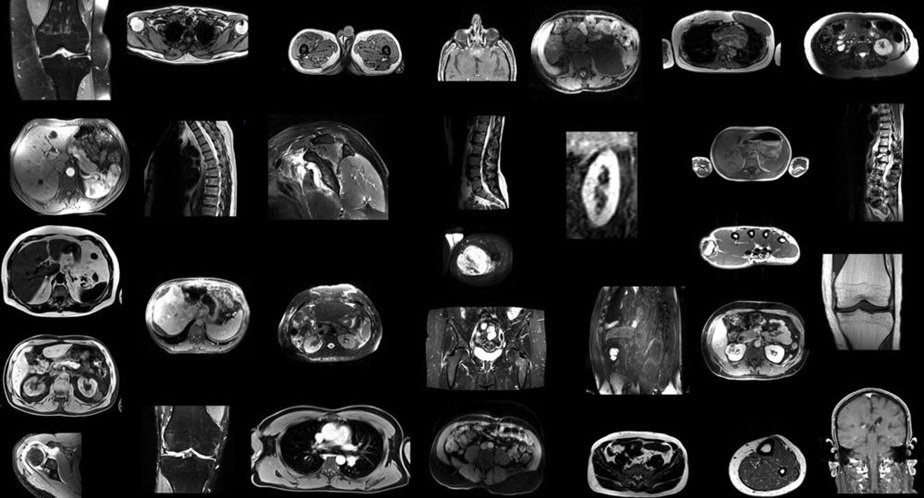
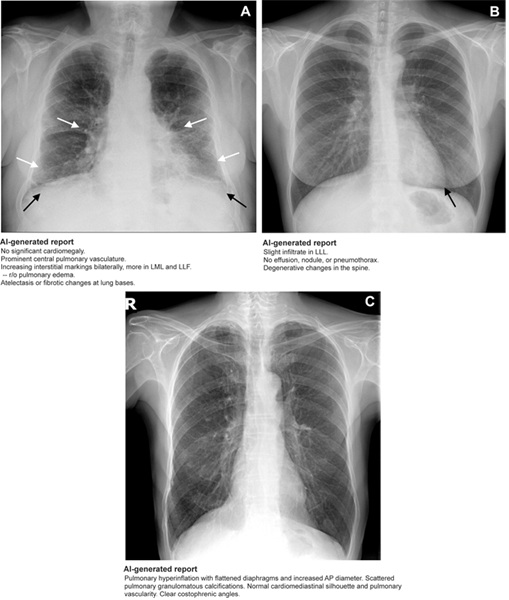
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a crucial role in providing detailed images of the human body, making it essential for diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions, from neurological disorders to musculoskeletal injuries. To interpret MRI images in depth, various anatomical structures such as organs, muscles, and bones are outlined or marked, a process known as segmentation. Traditionally, MRI images have been segmented manually, which is time-consuming, requires significant effort from radiologists, and is subject to variability between different readers. Automated systems offer the potential to reduce the radiologist's workload, minimize human errors, and deliver more consistent, reproducible results. Researchers have now developed and tested a robust artificial intelligence (AI) model capable of automatically segmenting major anatomical structures in MRI images, regardless of the sequence. In a study published in the journal Radiology, the AI model outperformed other publicly available tools.
Researchers at University Hospital Basel (Basel, Switzerland) developed an open-source automated segmentation tool called TotalSegmentator MRI, built on nnU-Net, a self-configuring framework that has set new benchmarks in medical image segmentation. This tool can adapt to new datasets with minimal user intervention, automatically adjusting its architecture, preprocessing, and training strategies to optimize performance. A similar model for CT (TotalSegmentator CT) is already in use by over 300,000 users worldwide, processing more than 100,000 CT images daily. In their retrospective study, the researchers trained TotalSegmentator MRI to provide sequence-independent segmentation of major anatomical structures using a randomly sampled dataset of 616 MRI and 527 CT exams.
The training set included segmentation data for 80 anatomical structures, which are commonly used for tasks such as measuring volume, characterizing diseases, planning surgeries, and conducting opportunistic screenings. To assess the model’s performance, Dice scores—metrics that measure the similarity between two sets of data—were calculated by comparing the predicted segmentations to the reference standards set by radiologists. The model performed well across all 80 structures, achieving a Dice score of 0.839 on an internal MRI test set. It significantly outperformed two publicly available segmentation models, with scores of 0.862, 0.838, and 0.560, respectively, and matched the performance of TotalSegmentator CT. Beyond research and AI product development, the researchers believe the model has the potential to be used clinically for treatment planning, monitoring disease progression, and conducting opportunistic screenings.
“We used a lot more data and segmented many more organs, bones and muscles than has been previously done. Our model also works across different MRI scanners and image acquisition settings,” said Jakob Wasserthal, Ph.D., Radiology Department research scientist at University Hospital Basel. “To our knowledge, our model is the only one that can automatically segment the highest number of structures on MRIs of any sequence. It’s a tool that helps improve radiologists’ work, makes measurements more precise and enables other measurements to be done that would have taken too much time to do manually.”
Latest MRI News
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- New Research Supports Routine Brain MRI Screening in Asymptomatic Late-Stage Breast Cancer Patients
- Revolutionary Portable Device Performs Rapid MRI-Based Stroke Imaging at Patient's Bedside
- AI Predicts After-Effects of Brain Tumor Surgery from MRI Scans
- MRI-First Strategy for Prostate Cancer Detection Proven Safe
- First-Of-Its-Kind 10' x 48' Mobile MRI Scanner Transforms User and Patient Experience
- New Model Makes MRI More Accurate and Reliable
- New Scan Method Shows Effects of Treatment on Lung Function in Real Time
- Simple Scan Could Identify Patients at Risk for Serious Heart Problems
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read more
AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that women in middle age and older undergo a mammogram, which is an X-ray of the breast, every one or two years to screen for breast cancer.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read more
Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
Lung infections can be life-threatening for patients with weakened immune systems, making timely diagnosis crucial. While CT scans are considered the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, repeated scans... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more