Nonlinear Metamaterials Could Revolutionize MRI Scanning
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 20 Nov 2019 |
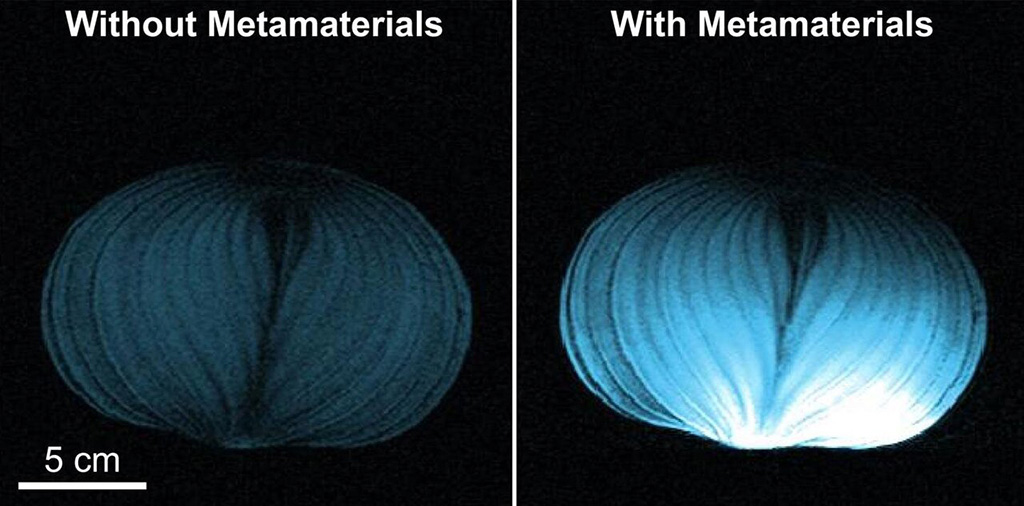
Image: Intelligent metamaterials Enhance MRI images (Photo courtesy of BU)
A new intelligent metamaterial could make the entire magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) process faster, safer, and more accessible to patients.
Developed by researchers at Boston University (BU; MA, USA), the coupled nonlinear metamaterial (NLMM) features a self‐adaptive response that amplifies the magnetic field commiserate to the resonance of the radio‐frequency (RF) excitation strength. The NLMM is suppressed in response to higher degrees of RF and recovers during a low excitation strength phase, thus increasing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) 10-fold, greatly enhancing image quality and reducing scan time, and thus opening up a new way to obtain crisper MRI images at very low cost.
The nonlinear response of the NLMM behavior is passive, selectively boosting low-energy RF emissions from the patient's body in normal mode, and turning itself off during the millisecond bursts of high-energy RF transmission from the MRI machine. The off-time, which last just a few milliseconds, allows intelligent NLMM to enhance the energy sent back to the MRI. It also diminishes the patient's overall exposure to radio wave radiation and mitigates potential safety concerns. The study was published on October 30, 2019, in Advanced Materials.
“The intelligent metamaterial consists of an array of metallic helical resonators closely packed with a passive sensor,” said lead author professor of radiology Xiaoguang Zhao, MD. “When the high-energy radio waves are coming in, the metamaterial detects the high energy level and turns off the resonance automatically. With low-energy radio excitation, the metamaterial turns on the resonance and enhances the magnetic component of the radio wave. We can now build smart materials that can interact with radio waves intelligently, enhancing the wanted signal while letting the unwanted signal go.”
MRI represents a powerful diagnostic tool in the armamentarium of modern healthcare that is widely applied across a spectrum of diseases, from stroke to cancer imaging and beyond. It can be used to generate images from a range of tissue properties without ionizing radiation, resulting in an inherently high degree of tissue contrast. Chief among the performance metrics of MRI systems is SNR, which may be leveraged to boost overall acquisition performance, from image resolution to the efficiency of image acquisition, and has been demonstrated to improve anatomic delineation and detection of pathology.
Related Links:
Boston University
Developed by researchers at Boston University (BU; MA, USA), the coupled nonlinear metamaterial (NLMM) features a self‐adaptive response that amplifies the magnetic field commiserate to the resonance of the radio‐frequency (RF) excitation strength. The NLMM is suppressed in response to higher degrees of RF and recovers during a low excitation strength phase, thus increasing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) 10-fold, greatly enhancing image quality and reducing scan time, and thus opening up a new way to obtain crisper MRI images at very low cost.
The nonlinear response of the NLMM behavior is passive, selectively boosting low-energy RF emissions from the patient's body in normal mode, and turning itself off during the millisecond bursts of high-energy RF transmission from the MRI machine. The off-time, which last just a few milliseconds, allows intelligent NLMM to enhance the energy sent back to the MRI. It also diminishes the patient's overall exposure to radio wave radiation and mitigates potential safety concerns. The study was published on October 30, 2019, in Advanced Materials.
“The intelligent metamaterial consists of an array of metallic helical resonators closely packed with a passive sensor,” said lead author professor of radiology Xiaoguang Zhao, MD. “When the high-energy radio waves are coming in, the metamaterial detects the high energy level and turns off the resonance automatically. With low-energy radio excitation, the metamaterial turns on the resonance and enhances the magnetic component of the radio wave. We can now build smart materials that can interact with radio waves intelligently, enhancing the wanted signal while letting the unwanted signal go.”
MRI represents a powerful diagnostic tool in the armamentarium of modern healthcare that is widely applied across a spectrum of diseases, from stroke to cancer imaging and beyond. It can be used to generate images from a range of tissue properties without ionizing radiation, resulting in an inherently high degree of tissue contrast. Chief among the performance metrics of MRI systems is SNR, which may be leveraged to boost overall acquisition performance, from image resolution to the efficiency of image acquisition, and has been demonstrated to improve anatomic delineation and detection of pathology.
Related Links:
Boston University
Latest MRI News
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
- New Research Supports Routine Brain MRI Screening in Asymptomatic Late-Stage Breast Cancer Patients
- Revolutionary Portable Device Performs Rapid MRI-Based Stroke Imaging at Patient's Bedside
- AI Predicts After-Effects of Brain Tumor Surgery from MRI Scans
- MRI-First Strategy for Prostate Cancer Detection Proven Safe
- First-Of-Its-Kind 10' x 48' Mobile MRI Scanner Transforms User and Patient Experience
- New Model Makes MRI More Accurate and Reliable
- New Scan Method Shows Effects of Treatment on Lung Function in Real Time
- Simple Scan Could Identify Patients at Risk for Serious Heart Problems
- Pioneering MRI Technique Detects Pre-Malignant Pancreatic Lesions for The First Time
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
A new study has revealed that an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solution significantly improves cancer detection in single-reader mammography settings without increasing recall rates, offering a... Read more
Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
For many years, healthcare professionals have depended on traditional 2D X-rays to diagnose common bone fractures, though small fractures or soft tissue damage, such as cancers, can often be missed.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
Echocardiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses ultrasound to visualize the heart and its associated structures. This imaging test is commonly used as an early screening method when doctors suspect... Read more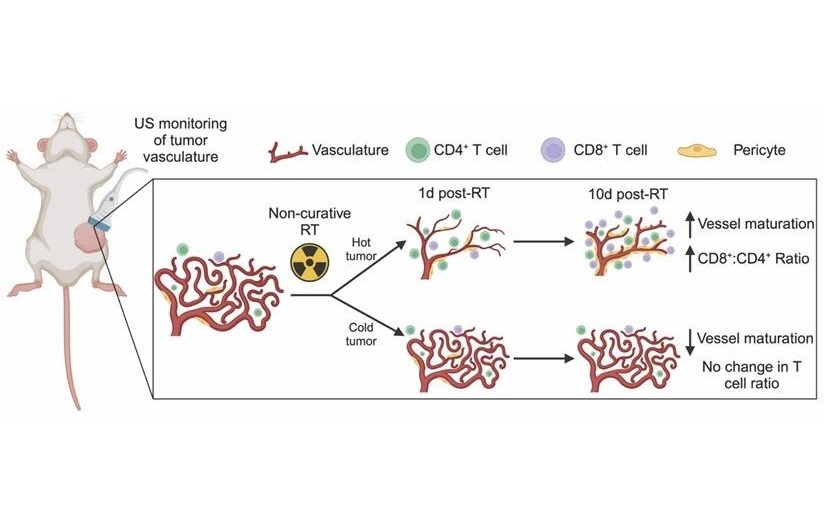
Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
While immunotherapy holds promise in the fight against triple-negative breast cancer, many patients fail to respond to current treatments. A major challenge has been predicting and monitoring how individual... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read more
Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease, are often diagnosed only after physical symptoms appear, by which time treatment may no longer be effective.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
Lung cancer impacts over 48,000 individuals in the UK annually, and early detection is key to improving survival rates. The UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) trial has already shown that low-dose CT (LDCT)... Read more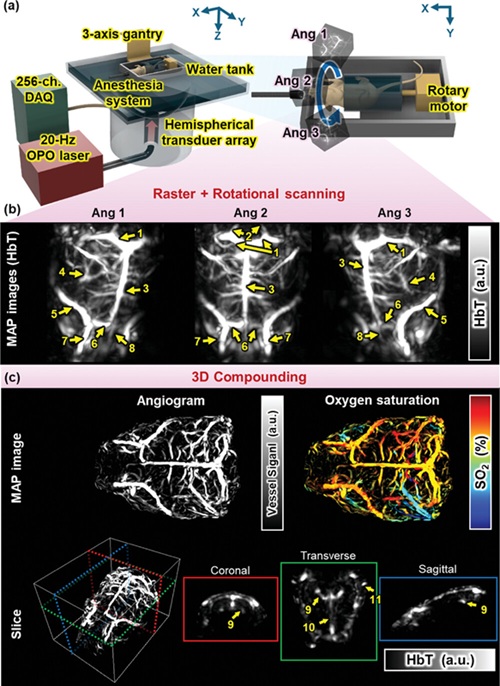
Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
Stroke is the second leading cause of death globally, claiming millions of lives each year. Ischemic stroke, in particular, occurs when a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain becomes blocked.... Read more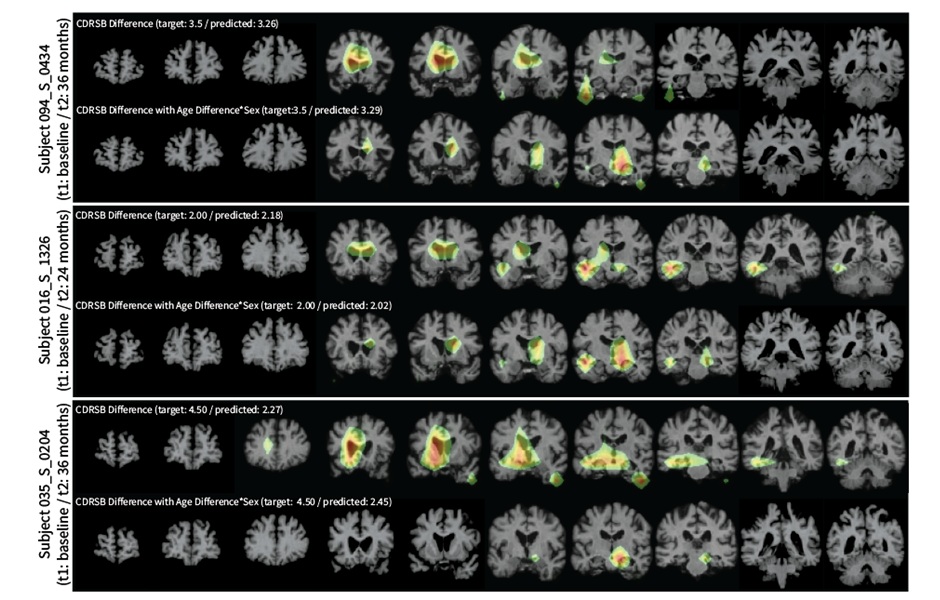
AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
Traditional approaches for analyzing longitudinal image datasets typically require significant customization and extensive pre-processing. For instance, in studies of the brain, researchers often begin... Read more
New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
Cancers of the mouth, nose, and throat are becoming increasingly common in the U.S., particularly among younger individuals. Approximately 60,000 new cases are diagnosed annually, with 20% of these cases... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













![Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242) Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242)](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-24/Brugarolas_F8.large.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpeg)