MRI
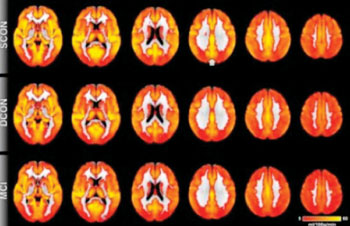
Arterial Spin Labeling MRI Identifies Evidence of Cognitive Decline Before Symptoms Present
A type of magnetic resonance imaging technology is being used to identify signs of cognitive decline in the brain even before symptoms appear. The technique has the potential to be used as a biomarker in very early diagnosis of preclinical dementia. More...16 Oct 2014
Gray Matter Volume in Brain Region Can Predict Risk Tolerance
Using whole-brain analysis, scientists discovered that the gray matter volume of a region in the right posterior parietal cortex of the brain was significantly predictive of individual risk attitudes. Men and women with higher grey matter volume in this region exhibited less risk aversion. The findings may clarify why risk tolerance decreases with age. More...09 Oct 2014
fMRI Neuro Scans Reveal Gray Matter Disparities in Media Devices Multitaskers
By simultaneously using laptops, cell phones, and other media devices, people could be changing their brain structure. A study reveals that individuals who frequently use several media devices used concurrently have lower gray-matter density in one specific region of the brain compared to those who use just one device occasionally. More...07 Oct 2014
MRI Technology Enables Noninvasive Monitoring of Emergent Cell Therapies
Cellular therapeutics, the application of using intact cells to treat and cure disease, is an important potential new therapeutic application, but it is hampered by the inability of clinicians and scientists to effectively monitor the destination, movements, and perseverance of these cells in patients without having to use invasive procedures, such as tissue sampling. More...07 Oct 2014
In Other News
MRI Measures Knee Geometry and Its Role in Severe Knee Injuries
MRI Technology Designed for Diagnosing Painful Back Disorder
fMRI Identifies Asymptomatic Individuals at Risk for Stroke
Neuroscientists Differentiate Patients in Ongoing Vegetative State

World’s First Wearable Prostate Coil Facilitates Simple and Accurate Positioning
Dedicated Diffusion Tensor Imaging Helps Predict Effects of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
MRI Helps to Identify and Quantify Fat in the Liver
fMRI Shows Neural Compensation Found in Individuals with Alzheimer’s-Related Protein
Macromolecular Proton Fraction Mapping and MRI Reveal That Loss of Myelin Denotes Severity of Multiple Sclerosis
MRI and PET Used with Solid Tumor Response Evaluation Criteria to Track Treatment in Bone Metastases
Dyslexic Patients Shown to Have Disordered Network Connections in the Brain
Brain Process Underlying Recognition of Hand Gestures Found to Develop Even When Blind
New Cardiology Imaging Tools Include MRI Myocardial Tissue Quantification to Help Fight Cardiovascular Disease
Neuro-MRI Scanning Reveals Disparities Between Imagining and Remembering
fMRI Shows Earlier Depression Can Lead to Hyperconnected Brain Networks in Young Adults
Nanotechnology Provides an Armory of Imaging and Therapeutic Applications
Transarterial Chemoembolization Contrast Agent Approved by French National Agency for Liver Cancer
Balance Board Triggers Favorable Changes in Multiple Sclerosis Patients’ Brains
Physically Fit Children Have More Robust Brain White Matter
MRI Tracks Infant Brain Growth in First Months of Life
Diffusion-Weighted MRI Becoming Major Tool to Diagnose Patients with Transient Ischemic Attacks
Ultrahigh-Field fMRI Findings May Help Patients Recover from Spinal Cord Injury
MRI Guidance, Remote-Controlled Catheter Technology May Improve Visualization of the Brain During Stroke Treatment
MedImaging's MRI channel in addition to reporting on MR hardware, informs about the many magnetic resonance applications possible with the technique notably MRI, fMRI, diffusion MRI, MR angiography, MR guided surgery, in addition to industry developments, and safety issues.











