Ultrasound-Activated Hydrogel Could Revolutionize Drug Delivery for Medical Applications
Posted on 30 Sep 2024
Researchers have created a composite hydrogel that enables sustained and consistent drug release, triggered by ultrasound. This breakthrough could transform drug delivery for numerous medical applications where maintaining constant drug levels is essential for optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Developed by researchers at Michigan Medicine (Ann Arbor, MI, USA), the composite is known as an acoustically responsive scaffold and utilizes a fibrin hydrogel matrix. Upon exposure to ultrasound, an emulsion embedded in the hydrogel vaporizes into bubbles, releasing the encapsulated drug. While current drug delivery systems, such as osmotic pumps, can provide zero-order release—delivering a constant drug dose over time—they often have limitations that this fibrin hydrogel can address. The ability to control drug release through ultrasound allows for sustained zero-order release, providing a consistent drug level over an extended period. This approach could improve treatment effectiveness and reduce side effects associated with fluctuating drug concentrations. A key advantage is the use of fibrin, a biocompatible material that naturally degrades in the body, eliminating the need for surgical removal after treatment, which is sometimes required with other implantable systems.
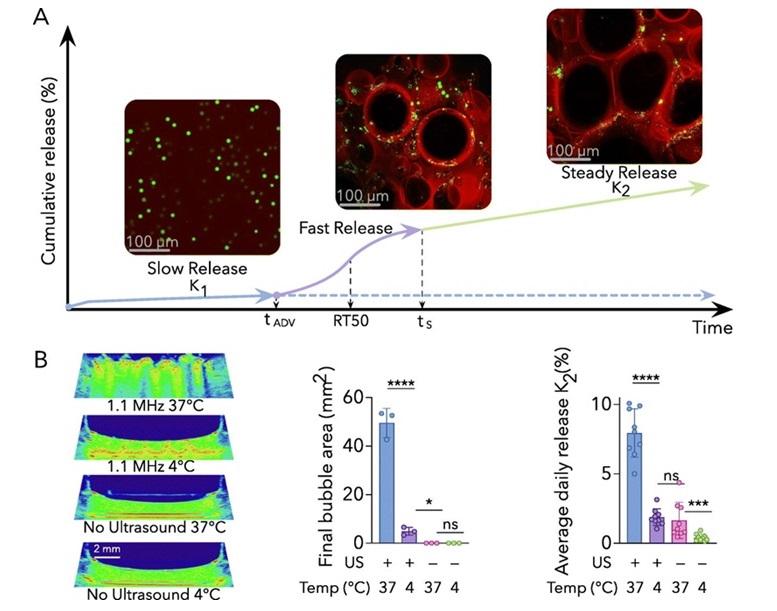
In the study published in the October 2024 issue of the Journal of Controlled Release, the researchers developed stepwise equations to describe the multi-phase release behavior of the acoustically responsive scaffolds. This process includes an initial rapid release triggered by ultrasound, followed by a steady, zero-order release phase. These equations offer a new framework for designing and optimizing ultrasound-triggered drug delivery systems. The research team had previously used these scaffolds to promote blood vessel growth. Expanding this technology to drug delivery brings several benefits, such as on-demand release, personalized treatment plans, and non-invasive dose adjustments. The team is now working on acoustically responsive scaffolds that can sequentially deliver multiple growth factors, potentially paving the way for more advanced applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
“Having a mathematical model that accurately describes the release process from the ARS is crucial for ultimately personalizing treatment,” said Mario L. Fabiilli, Ph.D., principal investigator within the Ultrasound Laboratory and senior author on the paper. “In the future, these equations will empower us to precisely fine tune the drug dose non-invasively to meet individual patient needs.”
Related Links:
Michigan Medicine














