AI Imaging Analysis Deciphers Ultrasound-Based Heart Scans
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 26 Nov 2019
An automated cardiac analysis platform based on artificial intelligence (AI) aids early detection of cardiovascular disease (CVD), helping clinicians improve patient care and outcomes.Posted on 26 Nov 2019
The Ultromics (Oxford, United Kingdom) EchoGo Core applies AI to calculate left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left ventricular volumes (LVV) and automated cardiac strain in order to automate analysis and quantification of ultrasound echocardiograms. The images are automatically uploaded to the Ultromics HUB, with all data exchanges de-identified to keep patient’s data private. The autonomous platform then automatically detects image type, heart cycle, and contouring in order to calculate key cardiac parameters.
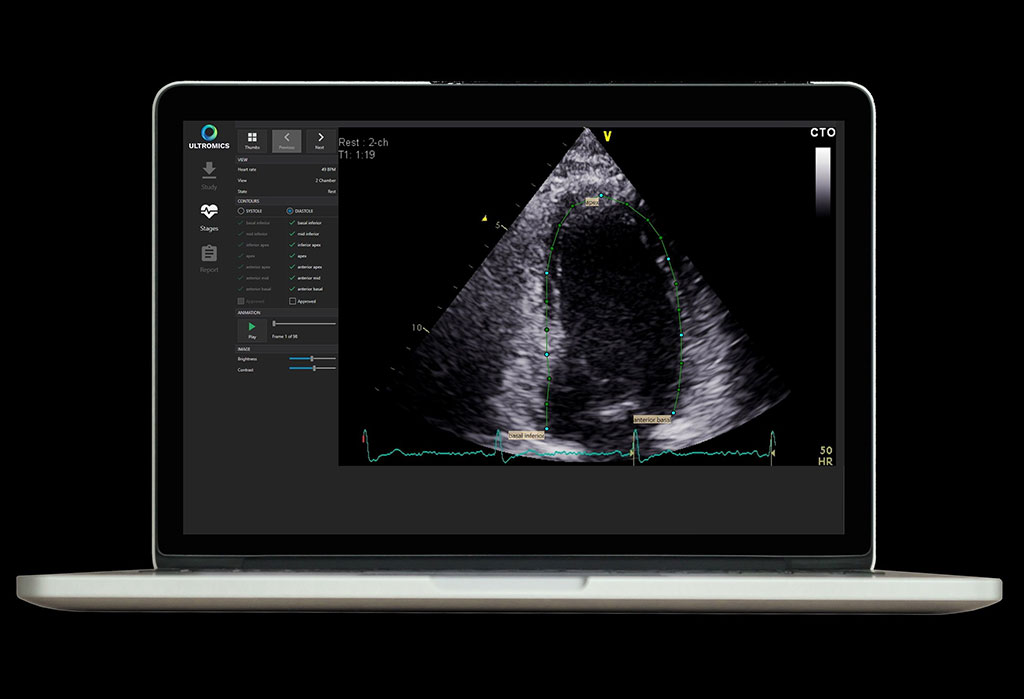
Image: Auto contouring generated by EchoGo, calculating key cardiac parameters (Photo courtesy of Ultromics)
A training model is then applied to predict CVD probabilities, and a report is generated. The technology uses topological analysis in order to identify thousands of data points from a single echocardiogram, drawing on information from a databank of over 120,000 echocardiogram images. The vendor-neutral platform integrates into the medical imaging environment, seamlessly providing clinicians with results as part of the routine diagnostic workflow.
“Strain has shown to be very valuable in cardiovascular diagnostics, and has been demonstrated in published studies to be linked with earlier detection of disease and improved patient outcomes,” said Ross Upton, founder and CEO of Ultromics. “This is an incredibly exciting step towards the future of healthcare, EchoGo will help clinicians make more accurate and informed decisions to improve patient care delivery. It's truly a watershed moment for Ultromics.”
Clinicians currently rely on echocardiograms as a diagnostic tool, analyzing a handful of data points with the naked eye to identify patterns and abnormalities that are characteristic of CVD. The problem is this takes time, and is entirely reliant on the training and expertise of the operator. When the operator is experienced the test is reasonably reliable, but expertise levels vary significantly, and training clinicians to interpret stress echocardiograms can take a number of years.
Related Links:
Ultromics






 Guided Devices.jpg)







