High-Energy Ultrasound Provides Clearer View of Liver Tumors
By MedImaging staff writers
Posted on 28 Jan 2008
Posted on 28 Jan 2008
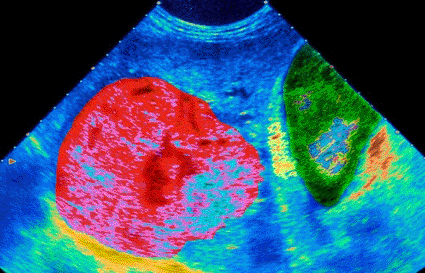
Image: Colored ultrasound scan of a malignant tumor (red) in a patient’s liver (Photo courtesy of Camal, ISM / SPL).
The study, performed by researchers from Duke University's Pratt School of Engineering (Durham, NC, USA), suggests that the imaging method known as acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) ultrasound might offer a new tool for screening patients at increased risk for liver cancers, according to the researchers. They reported that it might also play a useful role in guiding biopsy procedures and minimally invasive therapies geared at destroying cancerous tissues found deep in the abdomen.
The researchers reported their findings January 7, 2008, in the journal Physics in Medicine and Biology. The work was funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA) with system support from Siemens Medical Solutions (Erlangen, Germany).
First developed six years ago by Duke biomedical engineers Drs. Gregg Trahey and Kathy Nightingale, ARFI uses high-energy sound waves to push on tissues like sonic fingers. A tracking beam then captures the movement of the tissue, providing a measure of its elasticity or stiffness.
"To our knowledge, these are the first images of abdominal malignancies in humans that show tissue elasticity,” said Dr. Trahey, professor of biomedical engineering, radiology, and medical physics at Duke. The preliminary findings have already led Siemens to pursue a product prototype that will combine traditional ultrasound with ARFI, he added.
Typically, primary liver cancers are soft while those that have metastasized from other organs are hard. ARFI may be able to tell the difference between hard and soft tumors, according to Dr. Trahey. "If borne out in further studies, [that discriminating ability] suggests that ARFI may be useful in guiding treatment decisions. All current imaging methods--including CT [computed tomography], MRI [magnetic resonance imaging], and ultrasound--have mediocre performance in the detection of early liver cancers,” Dr. Trahey added. "There is a potential role for ARFI because it is low cost and can be built on conventional ultrasound machines.”
Traditional ultrasound is now the guidance method of choice in many hospitals for procedures targeting the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and lymph nodes, according to Dr. Trahey. Ultrasound has advantages in that it is widely available, low cost, and does not expose patients to ionizing radiation. However, a considerable number of tumors are difficult to see with this technique, requiring physicians to resort to alternatives such as CT and MRI, which add to the complexity and cost.
In the new study, the researchers captured ARFI images of 12 tumors in nine patients, including seven liver and two kidney tumors, and compared them to conventional ultrasound. The ARFI images showed greater contrast than standard ultrasound, providing clearer definition of the edges of cancerous masses.
Related Links:
Duke University's Pratt School of Engineering













