Novel CT Scanner Converts Photons to Images Directly
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 14 Oct 2021
A new computerized tomography (CT) system transforms data from X-ray photons that pass through a patient's body directly into a detailed three-dimensional (3D) image.Posted on 14 Oct 2021
Unlike standard CT detectors, which convert x-rays into images in a two-step process, the Siemens Healthineers (Erlangen, Germany) NAEOTOM Alpha system does not require an imaging sensor; instead, it counts photons directly using an active detection layer made of cadmium telluride (CdTe) crystals. The x-ray photons are therefore converted directly into a digital signal. X-ray and contrast medium dose can thus be substantially reduced and energy information is not lost, resulting in increased image contrast and sharpness.
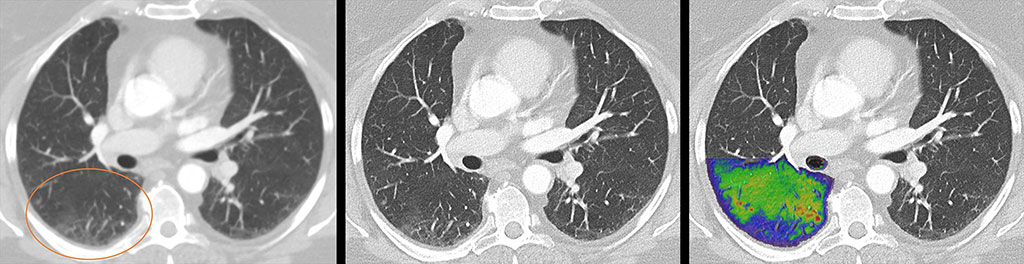
Image: NAEOTOM Alpha lung image of a post COVID19 patient (R), compared to conventional CT (L) (Photo courtesy of J. Ferda/ University Hospital Plzen)
In addition, the system uses two X-ray tubes and extremely short acquisition times. As a result, the examination of internal moving organs, such as the lungs and heart, is available with a previously unknown degree of accuracy. In order to handle and process the significantly higher data volumes, new approaches to data transfer and algorithms were developed, running on a powerful computing platform, allowing for the three dimensional (3D) images to be calculated and displayed in a matter of seconds.
“Thanks to the revolutionary images provided by photon-counting CTs, more people all over the world will benefit from precise and comprehensive examinations at low radiation and contrast dose, from oncological procedures and heart diagnostics to lung follow-up checks for respiratory illnesses,” stated Siemens Healthineers in a press release. “This adds a wealth of completely new clinically relevant information and improves image sharpness and contrast.”
CdTe has been studied as an energy detector material since 1960s. Its useful properties consist of a wide band gap (1.44 eV) with a high resistance (109 Ω), high atomic number (Cd: 48 and Te: 52), and high density (5.85 g/cm3) which provide better absorption characteristics. Because of the high absorption, CdTe can be applied for detection of energetic photons.
Related Links:
Siemens Healthineers





 Guided Devices.jpg)







