Novel PET Tracer Developed for Imaging Prostate Tumors
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 14 Aug 2017
A new PET tracer, called Carbon-11 labeled sarcosine (11C-sarcosine) has been used for the first time to image prostate cancer in a human being.Posted on 14 Aug 2017
According to the researchers the tracer could also be used to monitor targeted treatment of other cancers in the future.
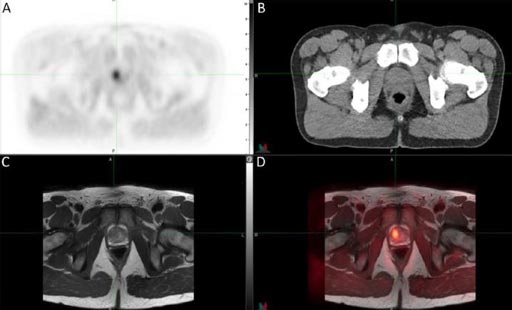
Image: A and B show trans-axial 11C-sarcosine hybrid PET/CT images of an adenocarcinoma. Image C shows a separately obtained T2-weighted MR sequence, and Image D shows the resulting PET/MRI registration (Photo courtesy of M. Piert et al., University of Michigan).
The researchers from the Division of Nuclear Medicine at the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor, MI, USA) compared the effectiveness of the new 11C-sarcosine tracer with an existing widely-used tracer called 11C-choline in two mouse models, and also carried out the first PET/CT (Computed Tomography) scan with 11C-sarcosine for imaging a human prostate cancer patient. The results of the study were published online in the August 1, 2017, issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Sarcosine is partly responsible for the aggressiveness and progression of prostate cancer and enters cells via Proton-coupled Amino acid Transporters (PAT).
The results of the study showed that in preclinical models 11C-sarcosine could produce high-contrast images of a human prostate cancer, and that 11C-sarcosine PET tumor-to-background ratios were significantly higher than those for 11C-choline. The researchers concluded that 11C-sarcosine has potential benefits over 11C-choline, and is a viable prostate cancer imaging tracer.
Professor of radiology at the University of Michigan Division of Nuclear Medicine, Morand Piert, MD, said, "Given the link between 11C-sarcosine cell uptake and PAT transport, the study provides first evidence that PAT expression can be elevated in prostate cancer. To our knowledge, this is the first radiotracer to interrogate the activity of PATs, which play a role as multi-purpose carriers with distinct roles in different cells. In the brain, these transporters are involved in the neuronal amino acid transport. In the intestinal tract, certain PATs play a role as nutrient and drug transporter."
Related Links:
University of Michigan














