Study Indicates CT Screening Could Improve Cardiac Treatments
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 21 Mar 2017
The results of a new review indicate that Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) screening for heart disease using Computed Tomography (CT), and other imaging technologies, could enable the early detection of coronary plaques, well before symptoms develop.Posted on 21 Mar 2017
In approximately 40-60% of cases, heart disease is found only when a patient has a heart attack, or dies. On the other hand screening for breast, lung, and colon cancer is in some cases routine. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the US, and currently patients are assessed using only historical data in conjunction with a standard blood test.
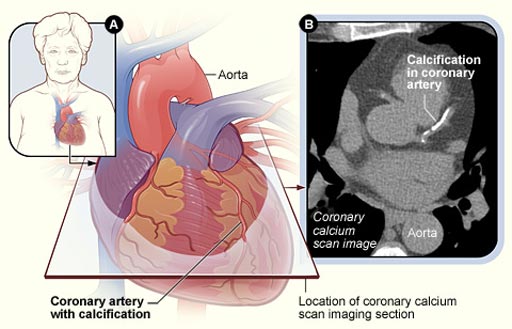
Image: A diagram of how a Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scan can be used for early detection of coronary plaques (Photo courtesy of the NIH).
The review was published in the March 4, 2017, issue of the journal JACC, and included an evaluation of five clinical trials, including 4,615 participants without signs of heart disease. In the first trial cardiac stress imaging was used, three of the trials used CAC cardiovascular imaging, and in the fifth trial researchers used coronary CT angiography. The results indicated that a CAC scan was far more accurate – a higher CAC score correlated with an increased risk for future heart disease.
Lead author of the study, chief academic officer Alan Rozanski, MD, division of cardiology, Mount Sinai St. Lukes Hospital, said, "The CAC scan can detect heart disease even decades before the symptoms of heart disease may first appear. Additionally, using current state-of-the-art scanners, CAC scans are associated with only very low radiation exposure, similar to that of a mammogram, and they are less costly than all other types of imaging. Given these advantages, there is increasing interest in determining whether the use of CAC scanning could lead to earlier and more effective treatment of heart disease. There is now sufficient evidence to support the routine use of CAC scanning for screening in clinical practice."














