Image-Guided Thoracic Surgery Effective for Removal of Small Lung Cancers
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 12 Jul 2016
The results of a clinical trial involving radiologists, and surgeons in a multidisciplinary team have shown that video-assisted surgery and real-time imaging guidance can be used together effectively to remove lung nodules without damaging healthy tissue.Posted on 12 Jul 2016
The clinical trial included 24 consecutive patients with lung nodules 0.6 cm to 1.8 cm in diameter. Some of the nodules were found after they underwent low-dose Computer Tomography (CT) screening. The surgeons successfully used the new real-time image-Guided Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (iVATS) procedure to remove the lung nodules from the patients using an acceptably low-range radiation dose.
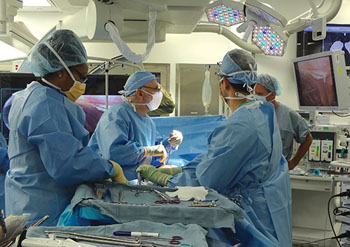
Image: The photo shows a surgeon performing an iVATS procedure in the AMIGO hybrid operating room (Photo courtesy of RSNA).
The iVATS procedure is being used in the Advanced Multimodality Image Guided Operating (AMIGO) hybrid operating room suite in the Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH; Boston, MA, USA). During the iVATS procedure the patient does not need to be relocated and can stay in the same position. The patient also undergoes only one general anesthesia. This reduces the time the patient spends in the operating room, and the risk of complications, and there is no migration of fiducial markers.
Study co-author, Ritu R. Gill, MD, MPH, associate radiologist, BWH said, “Thoracic surgery has evolved in the past decade toward minimally invasive surgery. Patients are living longer and may have more than one tumor in their lifetime. Surgical techniques are evolving to optimize resection and not take out more viable lung than is needed. This requires a multidisciplinary approach using intra-operative localization of lung nodules, allowing for targeted resection, decreasing operative times and morbidity. We now offer this procedure to patients as an optimal technique to remove small and ground glass and part-solid lung nodules.”
Related Links:
Brigham and Women’s Hospital














