New MRI Technologies Advance Image-Guided Radiotherapy
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 01 May 2018
New magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) pulse sequences and imaging enhancements further improve the precision by which radiotherapy (RT) is delivered to treat cancer.Posted on 01 May 2018
Designed for the ViewRay (Oakwood Village, OH, USA) MRIdian SmartVISION system and the MRIdian Linac RT system, the new T1w and T2w pulse sequences can deliver diagnostic-quality MRI during RT treatments by providing refined high-definition visualization and enhancing diagnostic contrast between cancerous and healthy tissues. Newly introduced diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) can also be used to distinguish between tumor and normal tissues, as well as to potentially assess and predict tumor response to RT.
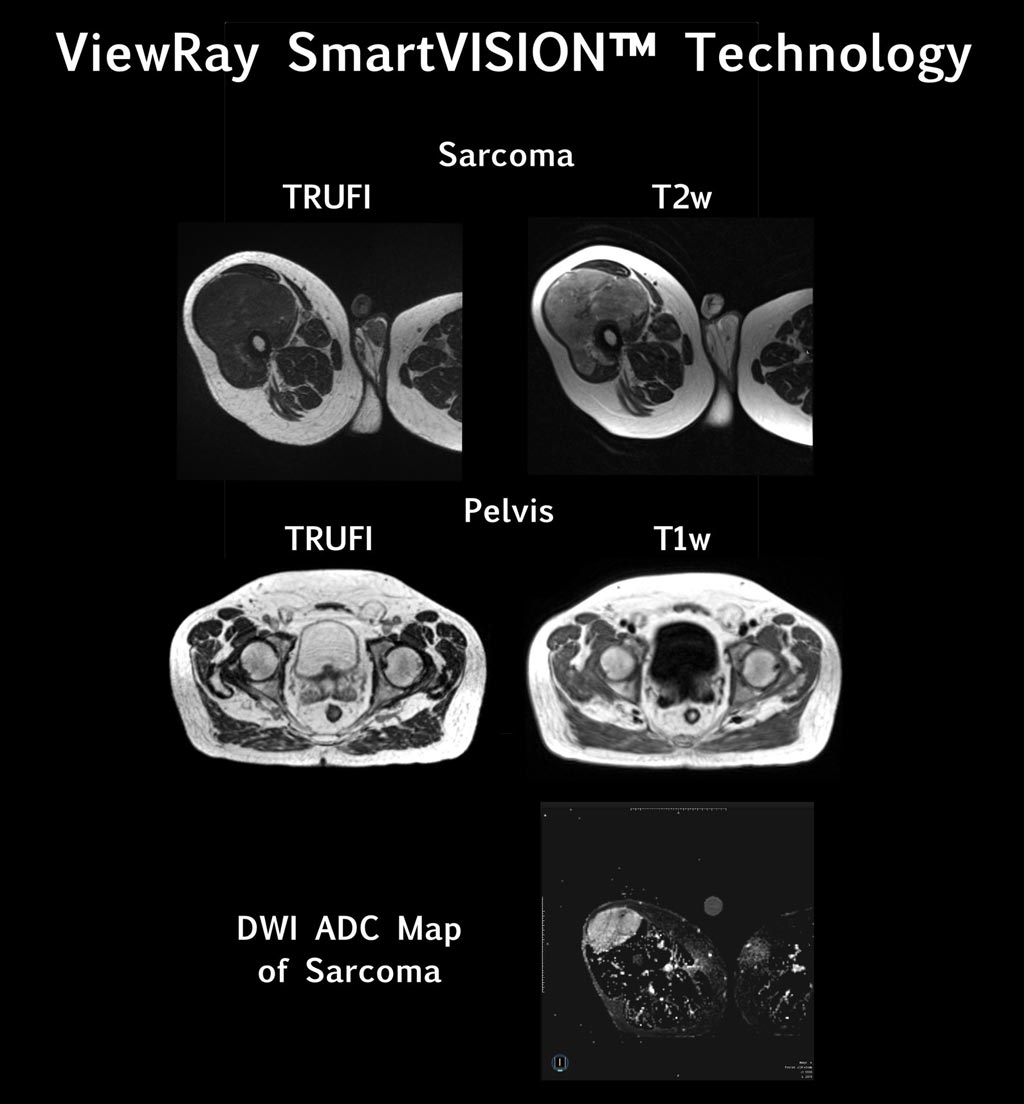
Image: MRIdian SmartVISION enhancements advance cancer RT (Photo courtesy of ViewRay).
Other enhancements to the SmartVISION system include a doubling of MRI speed (from four frames to eight frames per second), and twice the image resolution and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), helping to providing brighter, more detailed anatomical images. The system also continuously detects the shape and location of tumors and organs-at-risk (OAR) in real-time, automatically turning RT beams on and off when positional changes occur.
The MRIdian Linac system integrates real-time SmartVISION data and RT delivery via a rotating gantry assembly that a houses a compact inline S-band 6 MV standing wave linear accelerator (linac), with side-coupled cavities and double focused multi-leaf collimator technology; magnetic and radiofrequency (RF) shielding technology to isolate linac and MRI systems from each other; and a 0.35 T split magnet for unrestricted beam path, volumetric, and multi-planar soft tissue imaging. The system also includes a patient couch with three degrees of freedom, two in-room couch control panels, and a laser positioning system to facilitate initial patient setup.
A control console, located just outside the treatment room, is paired to an operator console for MRI acquisition, patient positioning, dose prediction, re-optimization, and real-time tumor tracking. An additional planning station helps define structures and constraints for planning and re-optimizing treatments, with support for plan reviews via a database server that contains patient and machine data, as well as software for creating treatment plans and managing the treatment delivery process.














