PET Scan May Help Personalize Cancer Treatment
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 14 Mar 2018
A same-day, noninvasive positron emission tomography (PET)-based imaging approach could help guide cancer treatment decisions and assess treatment response, claims a new study.Posted on 14 Mar 2018
Researchers at Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS; Princeton, NJ, USA) have developed a fluorine-18 (18F)-labeled engineered protein that targets the programmed death protein (PD-1), and its ligand PD-L1, which enables cancer to evade the immune system. The PD-L1 radioligand (18F-BMS-986192) was then evaluated in mice bearing bilateral PD-L1(-) and PD-L1(+) subcutaneous tumors in human tissues, as well as evaluating distribution, binding and radiation dosimetry in healthy cynomolgus monkey.
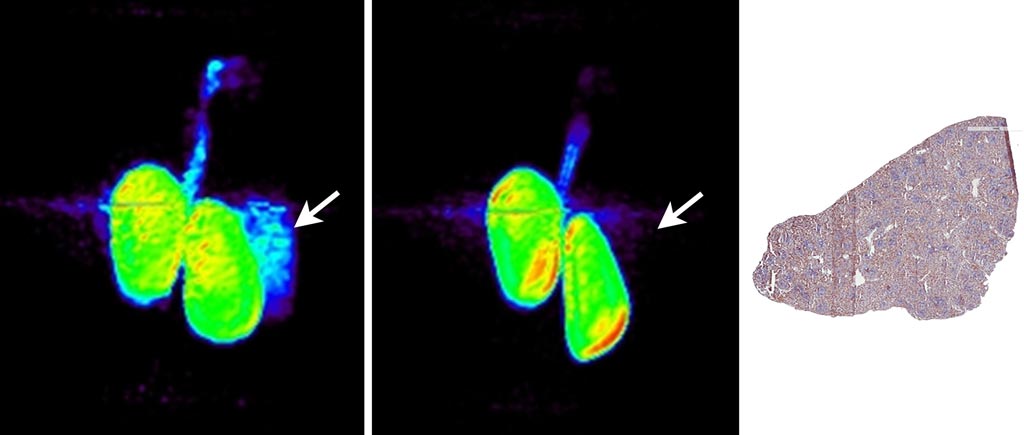
Image: PET images of kidneys and spleen 90 minutes post injection of 18F-BMS-986192 and anti-PD-L1 immunohistochemistry of healthy monkey spleen tissue (R) (Photo courtesy of David Donnelly/ BMS).
The results revealed that 18F-BMS-986192 bound to human and cynomolgus PD-L1 tumor tissues as a function of PD-L1 expression, with radioligand binding blocked in a dose-dependent manner. In-vivo PET imaging clearly visualized PD-L1 expression in the mice implanted with PD-L1(+) xenograft tumors. Two hours after dosing, a 3.5-fold-higher uptake was observed in the implanted mice, compared to control mice with PD-L1(–) tumors. Co-administration of an anti–PD-L1 adnectin reduced tumor uptake at two hours after injection by approximately 70%, demonstrating PD-L1–specific binding.
Biodistribution in the cynomolgus monkey showed binding in the spleen, which is rich in the PD-L1, with rapid blood clearance through the kidneys and bladder. Binding in the PD-L1(+) spleen was also reduced by co-administration of 18F-BMS-986192. According to the researchers, the results demonstrate the feasibility of the approach, and that radiation dosimetry estimates indicate that the tracer is safe to administer in human studies. The study was published in the March 2018 issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
“This approach represents an opportunity for physicians to noninvasively assess all of a patient's tumors for PD-L1 expression with a single PET scan and timely readout,” said lead author David Donnelly, PhD, of BMS Pharmaceutical Research and Development. “This may help guide treatment decisions and assess treatment response, to help identify the right treatment for the right patient at the right time and right dose.”
The PD-1 pathway is a cell surface receptor that plays an important role in down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T-cell inflammatory activity. The pathway guards against autoimmunity through a dual mechanism of promoting apoptosis in lymph node antigen-specific T-cells, while simultaneously reducing apoptosis in regulatory T-cells. Through these mechanisms, PD-1 inhibits the immune system, preventing autoimmune diseases, but it can also prevent the immune system from killing cancer cells.
Related Links:
Bristol-Myers Squibb














