Oxygen Microbubbles Sensitize Tumors to Radiation Therapy
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 14 Feb 2018
Injecting breast cancer with oxygen-filled microbubbles makes tumors three times more sensitive to radiation therapy (RT), according to a new study.Posted on 14 Feb 2018
Researchers at Thomas Jefferson University (TJU; Philadelphia, PA, USA), Drexel University (Philadelphia, PA, USA), and other institutions conducted a murine study in order to investigate if surfactant-shelled oxygen microbubbles injected intravenously into a tumor and “popped” by noninvasive ultrasound could elevate hypoxic tumor oxygen levels, thus making them more sensitive to RT. The researchers managed to show that the injected oxygen microbubbles successfully increased breast tumor oxygenation levels by 20 mmHg, significantly more than control injections of saline or untriggered oxygen microbubbles.
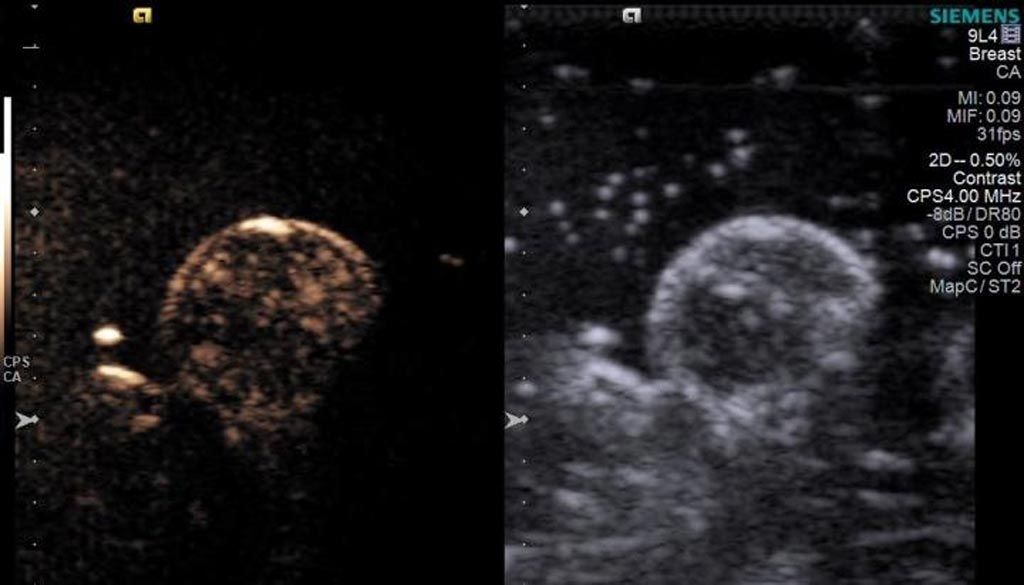
Image: A round breast tumor with oxygen microbubbles spread throughout the tumor (Photo courtesy of John Eisenbrey/ TJU).
Using photoacoustic imaging, the researchers also showed that using the microbubbles ensured that oxygen delivery was independent of hemoglobin transport, and thus effective in avascular regions of the tumor. Overcoming hypoxia by this method immediately prior to RT nearly triples RT radiosensitivity, resulting in roughly 30 days of improved tumor control, as well as statistically significant improvements in tumor growth and survival. The study was published on January 21, 2018, in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics.
“Finding a way to reverse oxygen deficiency in tumors has been a goal in radiation therapy for over 50 years. Oxygen microbubbles flush tumors with the gas, and make radiation therapy significantly more effective in animal models,” said senior author John Eisenbrey, PhD, of Jefferson University. “The very act of bursting these microbubbles within the tumor tissue seems to change the local physiology of the tumor and make cells generally more permeable to oxygen and potentially to chemotherapy as well.”
Microbubbles are bubbles smaller than one mm in diameter, but larger than one micrometer. Gas-filled microbubbles oscillate and vibrate when a sonic energy field is applied and may reflect ultrasound waves. But because gas bubbles in liquid lack stability and therefore quickly dissolve, microbubbles must be encapsulated with a solid shell made from a lipid or a protein, such as albumin.
Related Links:
Thomas Jefferson University
Drexel University













