New MRI Method Automatically Detects Placental Health during Pregnancy
Posted on 06 Feb 2023
Early monitoring of the placenta can improve detection and prevention of pregnancy complications, such as preterm birth, fetal growth disorders and preeclampsia. Currently, standard MRI analysis methods are not capable of detecting placental compartments, oxygen status and structural abnormalities. Now, a new method can process MRI scans to reveal the distinct compartments of the placenta, measure oxygen levels in each region and identify malformations in blood vessels (i.e., placental lesions).
In a study funded by the National Institutes of Health, researchers at Washington University in St. Louis (WUSTL, St. Louis, MI, USA) and University of Texas (UT) at Austin (Austin, TX, USA) have developed analysis methods for MRI scans that are generally performed in hospitals and healthcare facilities. These types of MRI scans do not need contrast agents, which are used only during pregnancy under limited circumstances. The machine learning method developed by the researchers automatically processes MRI data to visualize separate placental compartments, including the intervillous space (the area where maternal blood enters to provide nutrients and gas exchange), placental vessels and placental tissue. In contrast to the current MRI analysis methods, which can only measure placental oxygen as an average across the entire organ, the new method is capable of characterizing oxygen levels within these discrete compartments.
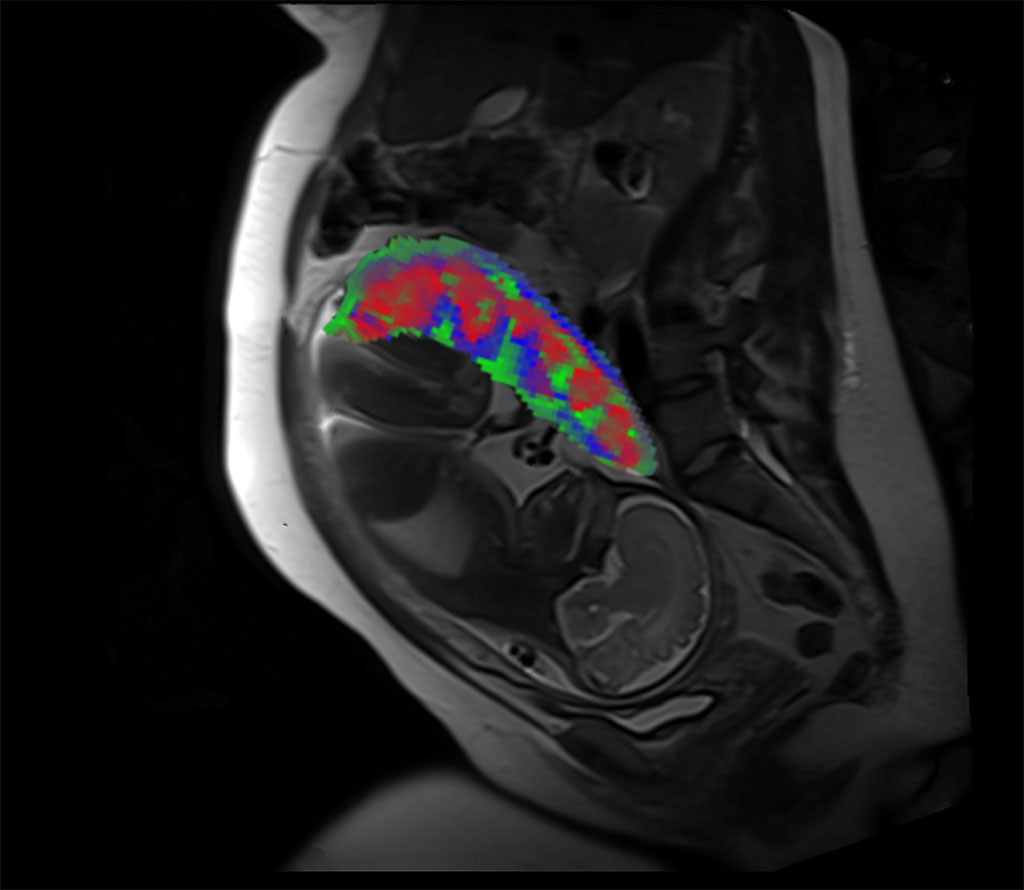
The researchers also used these region-specific measurements to find differences between 22 study participants with healthy pregnancies and five participants who went on to develop pregnancy complications. The team did observe some trends, indicating the potential use of their technique for detecting specific pregnancy complications, the researchers will be required to conduct further analysis among larger groups of study participants. Nevertheless, the new method can act as an objective, quantitative method for assessing placental health during pregnancy. After additional validation and refinement of the technique, it will be possible for healthcare providers to use the method as a tool to care of pregnant patients, especially those facing a risk of pregnancy complications.
Related Links:
WUSTL
UT at Austin