Structural MRI Can Help Predict Outcomes of Electroconvulsive Therapy
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 01 Jun 2016
Results from a non-randomized prospective study have shown that neuro-imaging techniques can be used to predict the therapeutic effectiveness of ElectroConvulsive Therapy (ECT) in individuals.Posted on 01 Jun 2016
ECT therapy treatment involves intentionally triggering a short seizure in the brain using small electric currents, and is performed under general anesthesia. The procedure can be used to treat certain mental illnesses, including acute major depressive disorder.
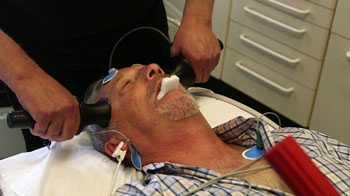
Image: A patient undergoing ECT treatment, which involves using small electric currents to trigger a short seizure in the brain (Photo courtesy of BBC Newsnight).
The research was published online in the May 4, 2016, issue of the journal JAMA Psychiatry. The goal of the researchers from the University of Muenster (Muenster, Germany) was to find out whether structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) could identify biomarkers that could accurately predict the response to ECT treatment.
In the study, the structure of grey matter of inpatients from Department of Psychiatry at the University of Muenster was assessed twice using a 3-T MRI scanner and voxel-based morphometry, at intervals of approximately 6 weeks. The study took place between March 11, 2010, and March 27, 2015. The patients included two groups with acute major depressive disorder, one of which received a series of ECT treatments and antidepressants (n = 24). The second group was treated with antidepressants (n = 23) alone. The researchers then compared both groups with a healthy control group (n = 21).
The researchers found that successful treatment with ECT therapy could be linked to a relatively small degree of structural impairment in the sub-genual cingulate cortex observed in neuroimaging before treatment.
Related Links:
University of Muenster