New Probe Tracks Osteoarthritis Development
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 25 Feb 2015
A new study has pioneered a technique to track the development of osteoarthritis in the initial and moderate stages of the disease. The technique could enable earlier diagnosis and management of the disease which affects millions, and is the leading cause of chronic disability in the United States.Posted on 25 Feb 2015
Researchers at the Tufts University School of Medicine (TUFS; Medford Somerville, MA USA) and the Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences at Tufts (Boston, MA, USA) carried out the study using male mice.
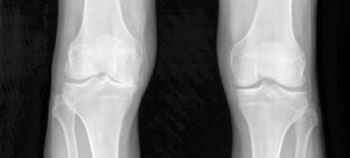
Image: New Possibilities for Osteoarthritis Detection Uncovered by Sackler Team (Photo courtesy of United States National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)).
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, is often the result of an injury or long term wear and tear to joints in the hip, hand, or knees. The disease is often detected late, when symptoms and pain begin.
The study, published in the February issue of Arthritis & Rheumatology used near-infrared fluorescent material as a probe, and optical imaging, to measure Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) enzyme activity and the changes leading to cartilage loss and osteoarthritis in joints over time. The study took images of the knees of 54 male mice over a two-month period and found that the signal from the fluorescent probe increased/brightened in the early to moderates stages of osteoarthritis.
Corresponding and senior author of the study, Li Zeng, PhD, reports that the next step is to monitor the fluorescent probe over a longer period of time to observe whether the same results are obtained during late stages the osteoarthritis. Li Zeng also hopes to use the probe to help develop osteoarthritis treatments for animals such as dogs for example.
Co-first author of the study, Shadi A. Esfahani, MD, MPH, said, “The fluorescent probe made it easy to see the activities that lead to cartilage breakdown in the initial and moderate stages of osteoarthritis, which is needed for early detection and adequate monitoring of the disease. To measure the probe’s signal, we used an optical imaging system, to noninvasively look inside the knee.”
Related Links:
Tufts University School of Medicine
Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences at Tufts












.jpg)