Potential New Tool for Cervical Cancer Detection
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 29 Dec 2014
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) has the potential to be a quicker, cheaper, and less-invasive method for detecting and staging cervical cancer (CC), according to a new study. Posted on 29 Dec 2014
Researchers at Central South University (Changsha, China) conducted 30 in vitro experiments with tissue samples representing different cancer stages, using PAI, a hybrid optical imaging technique that combines the high contrast of pure optical imaging with the high spatial resolution and the deep imaging depth of ultrasound. The technique involves short laser pulses, some of which are absorbed by the tissues and converted into heat, leading to rapid thermal expansion inside the tissues that produces ultrasonic waves. The generated waves are then detected by an ultrasonic sensor to form photoacoustic images of the tissues.
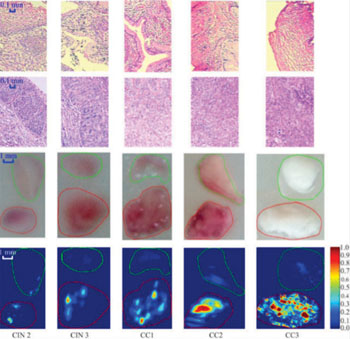
Image: Comparison of between normal cervical tissue (top), tissue lesion (second row), photographic image (third row) and corresponding DMAP images (fourth row) (Photo courtesy of Biomedical Optics Express).
In each of the experiments, the researchers embedded one section of normal cervical tissue and one section of cervical lesion (from the same person) in a cylindrical phantom for simultaneous PAI. Part of each sample was also sent to histological evaluation for cross-PAI. By processing all of the imaging data, the researchers obtained a depth maximum amplitude projection (DMAP) image, which shows the PAI contrast of the sample. The researchers used hemoglobin as the contrast agent, since PAI is highly sensitive to abnormal angiogenesis, a hallmark of CC tumors.
The obtained DMAP images were analyzed to evaluate the extent of the angiogenesis for different clinical stages of CC. The results showed stronger absorption from the cervical lesions, relative to that of normal tissue. The difference in mean optical absorption (MOA) between normal tissue and CC lesions showed a statistical significance, and the MOA of the CC lesions were closely related to the severity of CC. The study was published in the January 2015 issue of Biomedical Optics Express.
“Due to the higher hemoglobin concentration, abnormal angiogenesis has higher optical absorptions in certain wavelengths than normal tissues,” said lead author assistant professor of biomedical engineering Jiaying Xiao, PhD. “The technique is noninvasive and can detect the lesions in the cervical canal, an area conventional methods fail to observe. The photoacoustic imaging can also evaluate the invasion depth of cervical lesions more effectively.”
In current clinical practice, the diagnosis of CC is mainly through the cervical screening followed by a necessary biopsy, but this method is labor consuming and expensive, and can only detect superficial lesions around the external cervical orifice. In contrast, PAI is sensitive to the abnormal angiogenesis deep in the biological tissue, and may be capable for the intact scanning both around the external orifice and in cervical canal.
Related Links:
Central South University