Mammography AI Could Sharply Reduce Radiology Workload
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 12 Jul 2021
Using artificial intelligence (AI) in breast cancer screening could reduce the workload of radiologists by up to 70% without reducing cancer detection rates, according to a new study.Posted on 12 Jul 2021
The study, by researchers at Maimonides Institute for Biomedical Research (IMIBIC; Córdoba, Spain) and ScreenPoint Medical (Nijmegen, the Netherlands), compared a simulated AI triaging strategy using ScreenPoint’s Transpara AI software with double or single reading by radiologists in a retrospective analysis of 15,987 digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and digital mammography (DM) images from the Córdoba Tomosynthesis Screening Trial.
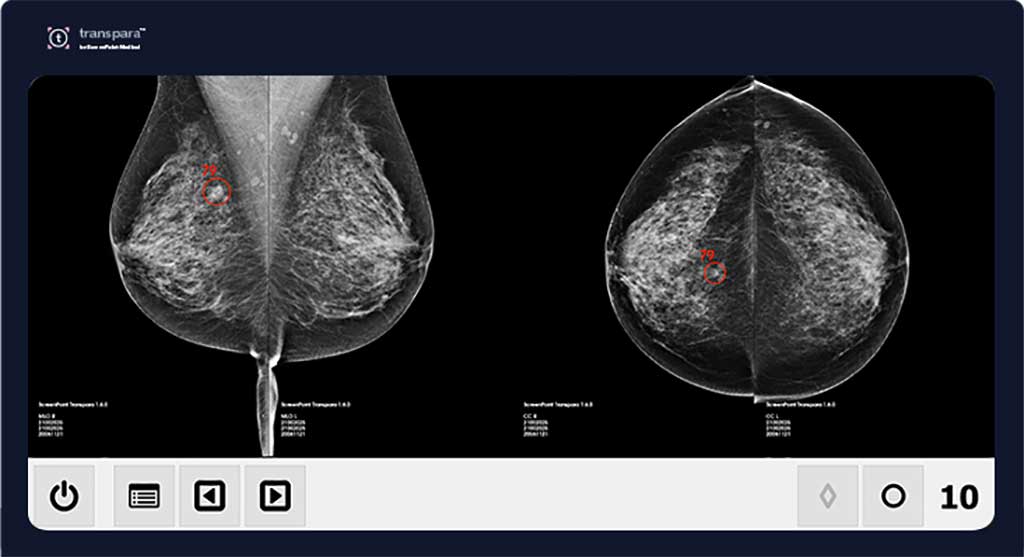
Image: Transpara AI can reduce mammography workload (Photo courtesy of ScreenPoint Medical)
The examinations included 98 screening-detected and 15 interval cancers. The results showed that in comparison with double reading of DBT images, AI with DBT would result in 72.5% less workload, non-inferior sensitivity, and a and 16.7% lower recall rate. Similar results were obtained for AI with DM; compared to the original double reading of DM images, AI with DM would result in 29.7% less workload, 25% higher sensitivity, and 27.1% lower recall rate. The study was published on May 4, 2021, in Radiology.
“DBT images can take twice as long for radiologists to read compared with DM. However, with AI, it may be possible to move from using digital mammograms to digital breast tomosynthesis,” said lead author radiologist José Luis Raya-Povedano, MD, of the IMIBIC Breast Cancer Unit. “The workflow of breast cancer screening programs could be improved, given the high workload and the high number of false-positive and false-negative assessments.”
Transpara is based on FusionAI, a combination of pathology, clinical imaging, X-ray physics, and deep learning (DL) techniques, designed to improve mammography reading accuracy, help interpretation of suspicious areas, increase confidence for normal and suspicious cases, and speed up reading of 2D and 3D mammograms.
Related Links:
Maimonides Institute for Biomedical Research
ScreenPoint Medical













