High-Definition Fiber Tracking Effectively Reveals Brain Anatomy
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 07 Aug 2012
High-definition fiber tracking (HDFT) provides full-color, precise images of the brain’s fiber network that accurately reflect brain anatomy observed in surgical and laboratory studies, according to a new report.Posted on 07 Aug 2012
Investigators from the University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) School of Medicine (UPMC; PA, USA) published their findings in the August 2012 issue of the journal Neurosurgery, which supported the idea that HDFT scans can provide valuable insights into patient symptoms and the prospect for recovery from brain injuries, and can help surgeons plan their approaches to remove tumors and abnormal blood vessels in the brain.
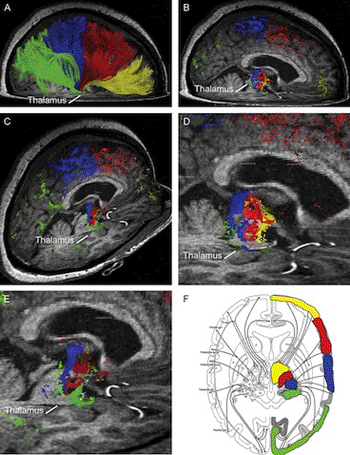
Image: High definition fiber tracking, or HDFT, images of the brain’s fiber network that accurately reflect brain anatomy observed in surgical and laboratory studies (Photo courtesy of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine).
When performing deep brain surgery, the neurosurgeon may need to cut or push brain fiber tracts, meaning the neuronal cables connecting the key brain areas, to get to a mass, according to Juan Fernandez-Miranda, MD, assistant professor, department of neurological surgery, Pitt School of Medicine. Depending on the location of the tumor and the surgical path, the surgeon takes to get to it, fiber tracts that control abilities such as memory, language, and motor function could be injured.
“Standard scans such as MRI [magnetic resonance imaging] or CT [computed tomography] can show us where a mass lies in the brain, but they cannot tell us whether a lesion is compressing or pushing aside brain fibers, or if it has already destroyed them,” Dr. Fernandez-Miranda said. “While the symptoms the patient is experiencing might give us some hints, we cannot be certain prior to surgery whether removing the mass will disrupt important brain pathways either near it or along our surgical route through brain tissue to get to it. Our study shows that HDFT is an imaging tool that can show us these fiber tracts so that we can make informed choices when we plan surgery.”
A sophisticated MR scanner is used to obtain data for HDFT images, which are based on the diffusion of water through brain cells that transmit nerve impulses. Similar to a cable of wires, each tract is comprised of many fibers and contains millions of neuronal connections. Other MR-based fiber tracking techniques, such as diffusion tensor imaging [DTI], cannot accurately follow a set of fibers when they cross another set, nor can they reveal the endpoints of the tract on the surface of the brain, said coauthor Walter Schneider, PhD, professor, Learning and Research Development Center (LRDC), department of psychology, University of Pittsburgh, who led the team that developed HDFT.
For the new study, Dr. Fernandez-Miranda and his colleagues obtained HDFT scans of 36 patients with brain lesions, including cancers, and six neurologically healthy individuals. They also dissected the fiber tracts, such as the language and motor pathways, of 20 normal postmortem human brains.
The investigators discovered that HDFT accurately replicated important anatomic features, including the topography of brain tissue; a region called the centrum semiovale, where multiple fiber tracts cross; the sharp curvature of the optic radiations that carry information to the visual cortex; and the endpoints on the brain’s surface of the branches of the arcuate fasciculus, which is involved in language processing.
For the second part of the study, the team conducted HDFT scans in 36 patients prior to surgery, along with the imaging studies that are typically done as part of the preoperative planning process. They then compared fiber involvement predicted by HDFT with what they found during surgery.
“The scans accurately distinguished between displacement and destruction of fibers by the mass,” said study coauthor Robert Friedlander, MD, professor and UPMC chair in Pitt’s department of neurological surgery. “Postoperative HDFT scans also revealed where surgical incisions had been made, further validating the technique’s imaging power.”
Dr. Friedlander added it is not yet known how much fiber loss must occur to appear as a disruption or to cause symptoms, or what constitutes irreversible brain damage. “Although there is more work we must do to optimally develop the technique, HDFT has great potential as a tool for neurosurgeons, neurologists and rehabilitation experts,” Dr. Friedlander said. “It is a practical way of doing computer-based dissection of the brains of our patients that can help us decide what the least invasive route to a mass will be, and what the consequences might be of being aggressive or conservative in the removal of a lesion.”
The team is continuing to assess HDFT’s potential in a range of studies.
Related Links:
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine














