Nuclear Medicine
MRI and PET Used with Solid Tumor Response Evaluation Criteria to Track Treatment in Bone Metastases
Imaging technologies are very useful in evaluating a patient’s response to cancer treatment, and this can be done quite effectively for most tumors using solid tumor response evaluation criteria. More...22 Sep 2014
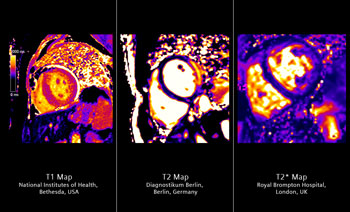
New Cardiology Imaging Tools Include MRI Myocardial Tissue Quantification Tool and to Help Fight Cardiovascular Diseases
New imaging tools have been designed for a more precise diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases using computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and molecular imaging, as well as utilizing a universal angiography system with sophisticated features for cardiology. More...10 Sep 2014
Nanotechnology Provides an Armory of Imaging and Therapeutic Applications
Scientists have created dynamic nanoparticles that could provide a range of applications to diagnose and treat cancer. Built on a simple-to-construct polymer base, these particles can be utilized as contrast agents to illuminate tumors for MRI and PET scans or deliver chemo and other therapies to kill tumors. More...08 Sep 2014
PET Imaging Reveals Brain Benefits from Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery
Imaging studies revealed that weight loss surgery has been found to suppress changes in brain metabolism associated with obesity and improve cognitive function involved in planning, strategizing, and organizing. More...31 Aug 2014
Identifying Brain Networks Using Metabolic Brain Imaging-Based Mapping Strategy
A new image-based strategy has been used to identify and gauge placebo effects in randomized clinical trials for brain disorders. The researchers employed a network mapping technique to identify specific brain circuits underlying the response to sham surgery in Parkinson’s disease. More...31 Jul 2014
In Other News
Soft Tissue Radiotherapy Real-Time Tracking Device Receives Approval
Simplified Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using PET Imaging and More Effective Criteria
Proton Therapy Has Better Outcome over IMRT for Advanced Head and Neck Cancers

SPECT/CT Technology Offers High Resolution and Quantitative Imaging
Four Imaging Approaches Can Differentiate Malignant and Benign Breast Tumors
NMR-Based Diabetes Risk Index Helps to Identify Normal-Weight Individuals at High Risk of Progressing to Type 2 Diabetes
Proton Therapy Provides Safe, Long-Term Treatment for Hodgkin Lymphoma
Molecular Imaging Provides Insights into Rheumatoid Arthritis
PET Imaging Used to Monitor Beta Cell Status in Type 1 Diabetes
SPECT/CT Plus Enzyme Found to Be Best Imaging Modality for Detecting Coronary Arterial Disease
New Tumor-Targeting Agent Images a Wide Range of Cancers

PET/CT System Enhances Disease Detection and Treatment Assessment
SPECT/CT Imaging Helps Choose Best Treatment for Low Back Pain
Presurgical SPECT/CT Imaging for Breast Cancer Reveals More Tumors Than Lymphoscintigraphy
PET/MR Found Best Imaging Modality for Detecting Coronary Arterial Disease
Taipei University to Install Proton Treatment Center
Patient-Friendly PET/CT System Provides Very Large Bore, Wide Field-of-View, and Fast Imaging
Molecular Breast Imaging Strategy Reveals More Tumors
Five Diverse Imaging Technologies Now Combined in One SPECT/PET/CT System
Simulations Demonstrate Neutron-Stimulated Emission CT and Gamma-Stimulated Emission CT to Be Safe
Enhanced PET Imaging Radiotracers Designed for Better Tracking of Disease
Re-Treating Lung Cancer with Radiotherapy Is Effective
Breath Analysis Provides Same Sensitivity, Twice the Specificity of PET Imaging Identifying Early Lung Cancer
The Nuclear Medicine channel of MedImaging brings the latest in research and clinical radiotherapy, proton therapy, PET-CT, SPECT, SQUID, radiopharmacology, scintillography, trends and safety concerns.








 Guided Devices.jpg)


