Radiography
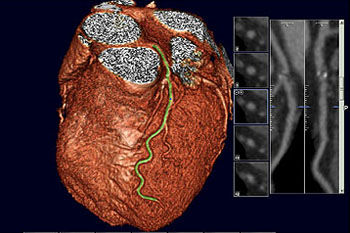
Heart Scans Only Useful in Specific Situations When Statins Are Prescribed
Research has revealed that with the existence of inexpensive statin therapy it is not necessary to perform a heart computed tomography imaging scan to measure how much plaque has accumulated in a patient’s coronary arteries, when patients have been taking statins. More...01 Apr 2014
US Clinicians Initiate Efforts to Optimize CT Safety
Clinicians and physicists in the United States have endorsed new strategies to make CT imaging safer, including implementation of a new metric for dose measurement, specific approaches to reduce exposure during needle biopsies, and ways to manage exposure protocols that differ by CT manufacturer. More...01 Apr 2014
In Other News
CT Scans Predict Chemotherapy Response in Pancreatic Cancer Patients
X-Ray Sector Surpasses USD 3 Billion Globally
Europe Welcomes Bayer’s Stellant with Certegra Workstation to Support the Radimetrics Enterprise Platform
Portuguese Cancer Center Becomes World’s First to Offer Innovative Radiosurgery Application
Aquilion ONE Second Generation Launches Advanced Features
Philip’s SkyFlow Removes the Grid in Mobile Radiography
GE Healthcare’s Dose Blueprint Launched Alongside EUROSAFE and the New EU Directive on Dose Management at ECR
Siemens Somatom Scope Saves Up to 65% on energy and 35% on Costs
European Initiative Established for Safe X-Ray Use
Wireless, Cassette-Sized Flat Panel Detector Designed for Digital Radiography
Researchers Employ High-Energy X-Ray to Image Living Cancer Cells
Limiting Radiation to Major Salivary Glands in Head and Neck Cancer Patients
CT Scans Shown Not to Interfere with Heart Rhythm Devices
Mobile C-Arm System Combines Ease of Use with Dose Management Features
Favorable Outcomes Seen for Advanced Stage Tonsil Cancer Using Unilateral Radiotherapy
French X-Ray Anode Company Enters Chinese Medical Imaging Market
First MR-Safe and CT-Compatible Neurosurgical Horseshoe Headrest Provides Nonrigid Positioning
Ultrafast CT Scanner Designed for Optimized Cardiology
Dressing Designed to Prevent Skin Reactions During Radiation Therapy
Findings of Canadian Mammography Study Disputed by American Radiology and Breast Imaging Societies
Partnership to Provide Surgical Navigation Capabilities to a Portable CT Scanner
Superbright, Fast X-Rays Can Visualize Just One Layer of Proteins
MR Radiation Oncology Suite Provides Consistent Patient Positioning, Effectively Characterizes Cancer
The MedImaging Radiology channel covers fluoroscopy, digital radiography, computerized tomography, mammography, interventional radiology, and other medical uses of X-ray imaging as well as related instrumentation, trends and safety issues.











