Robotic Magnetic System for PCI Could Minimize Physicians’ Exposure to X-Ray Radiation
Posted on 10 Jun 2022
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) involves introducing a guidewire through the large femoral artery in the groin or the radial artery in the wrist and expertly manipulating it until it reaches the largest blood vessel in the body, the aorta. A contrast agent is then injected into the aorta, where it spreads into the coronary arteries that feed the heart. X-ray images are then taken to pinpoint any blockages present in these arteries. This intervention requires a huge amount of skill and can still lead to vessel perforation. It also involves unnecessary exposure of the physician to X-ray radiation, as the procedure is conducted at the patient’s bedside. Now, researchers have developed a medical robotic apparatus that uses an external magnetic field to precisely and remotely control guidewires through tiny and tortuous blood vessels. The apparatus could also minimize the exposure of physicians to X-ray radiation while looking for and treating narrowed or blocked blood vessels
The system developed by a multidisciplinary team of robotics and electronic systems engineers working with cardiologists and materials scientists led by researchers at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST, Daegu, Korea) involves remotely controlling a magnetically steerable microrobotic guidewire by applying a controllable external magnetic field. The field is generated by an ‘electromagnetic actuation system’ made of eight electromagnets arranged in a hemispherical configuration under a surgical bed. The patient is meant to be placed on the bed, with the guidewire inserted into an artery and guided remotely by changing the magnetic field. The guidewire is made of a biocompatible silicone tube that can move through blood vessels with very little surface friction. The tip of the microrobotic tube encapsulates a neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet and hard-magnetic composites for magnetic steering.
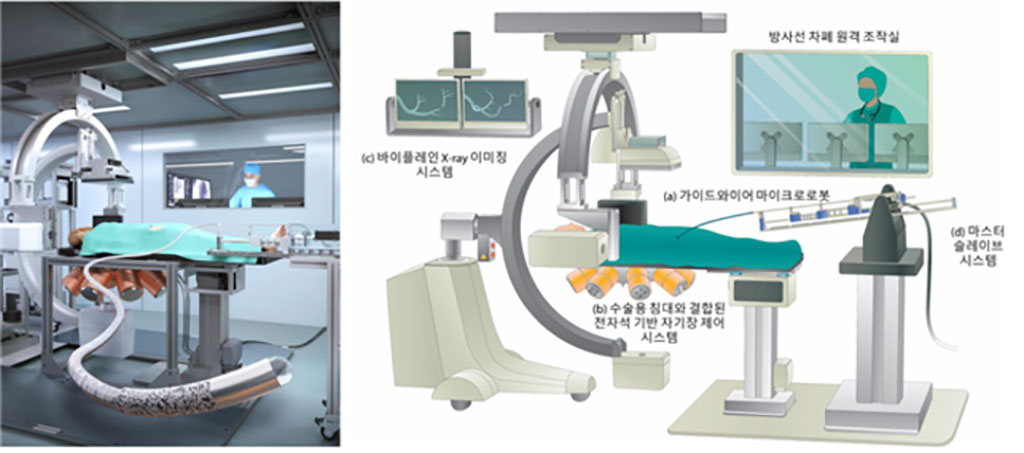
The researchers first tested the system using 2D- and 3D-printed blood vessel models. They then tested it in anaesthetized pigs, managing to remotely control the guidewires through small and tortuous arteries in the pelvis, kidneys and heart. More tests and improvements are still required, but the researchers are already planning to further modify their apparatus so it can also target vessels in the nervous system and lungs.
“Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, and it is very important to be able to diagnose and treat these diseases in the most minimally invasive way possible,” said DGIST robotics engineer Hongsoo Choi. “Our proposed electromagnetically controllable microrobotic interventional system (ECMIS) could reduce radiation exposure of physicians by empowering them to conduct the procedure remotely in an X-ray shielded control booth using low-strength magnetic fields. It also does not require the high level of training needed for conducting conventional PCIs.”
Related Links:
DGIST






 Guided Devices.jpg)







