PSMA PET Aids Decision Making in Prostate Cancer Treatment
Posted on 28 Mar 2023
Within 10 years after undergoing radical prostatectomy, approximately one-third of prostate cancer patients experience disease progression. Salvage radiation therapy (SRT) is a promising treatment option for these patients. However, current SRT follows contouring guidelines based on expert consensus, which do not utilize the information available from advanced imaging techniques like PSMA PET. Now, a recent study utilizing detailed PSMA PET mapping of cancer recurrence in the prostate bed has revealed that the current radiotherapy contouring guidelines miss a significant number of lesions and may result in unnecessary irradiation of healthy tissues.
The study by researchers at the University of Miami Health System (Miami, FL, USA) and University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA) involved the use of PSMA PET imaging to examine the recurrence patterns of the prostate bed in 127 prostate cancer patients with PSA persistence or biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy. Using the RTOG contouring guidelines, the researchers evaluated the location of recurrent lesions for each PSMA PET scan and established the clinical target volume (CTV). The lesions were subsequently classified as completely covered, partially covered, or not covered by the contouring guidelines. Of the patients, 53% had their recurrent lesions completely covered in the CTV, 34% were partially covered, while 13% were not covered at all. Additionally, some regions in the CTV showed no evidence of lesions. Following the study, the researchers are now advocating for a reevaluation of the prostate bed contouring guidelines to enhance patient outcomes.
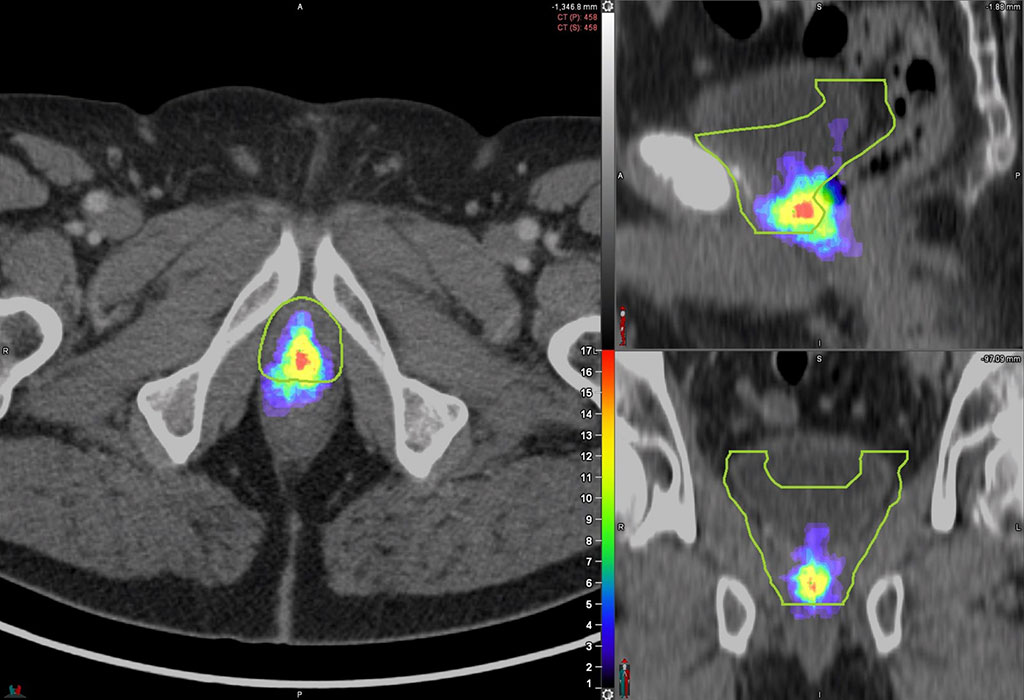
“We hope this study will help redefine prostate bed contouring guidelines for SRT to improve the outcomes of patients receiving radiotherapy post-radical surgery,” said Ida Sonni, MD, nuclear medicine physician and academic researcher in the Department of Radiological Sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles. “Our work confirms the crucial and growing role that nuclear medicine and molecular imaging have in guiding decision-making for cancer treatment. Nuclear medicine plays an essential part in the multidisciplinary management of patients with prostate cancer and facilitates the use of individualized, tailored treatments, which ultimately benefit all our patients.”
Related Links:
University of Miami Health System
UCLA














