New AI Tool Detects Possible Metastatic Breast Cancer by Improving MRI Sensitivity
Posted on 28 May 2024
Most breast cancer-related deaths are attributed to metastatic disease, with the initial site of metastasis often being an axillary lymph node. Accurately determining the nodal status is crucial for guiding treatment choices; however, traditional imaging methods alone lack the sensitivity required to definitively exclude axillary metastasis. Consequently, patients frequently need to undergo invasive procedures involving the injection of radioisotopes and dyes, followed by surgery to extract and examine the axillary nodes for the presence of cancer cells. Now, a pioneering artificial intelligence (AI) model that utilizes standard magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) along with machine learning, can identify axillary metastasis—the spread of cancer cells to the lymph nodes under the arms. This noninvasive approach has the potential to enhance the detection of breast cancer metastasis, potentially reducing the need for needle or surgical biopsies.
In a retrospective analysis, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center (Dallas, TX, USA) evaluated dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI scans from 350 breast cancer patients who had recently been diagnosed and whose nodal status was known. These images, combined with various clinical data, were employed to train the AI model to detect axillary metastasis using machine learning techniques. The results showed that the AI model was significantly more effective at identifying patients with axillary metastasis than either MRI or ultrasound. In practical application, this AI model could have prevented 51% of benign (noncancerous) or unnecessary surgical sentinel node biopsies while accurately identifying 95% of patients with axillary metastasis.
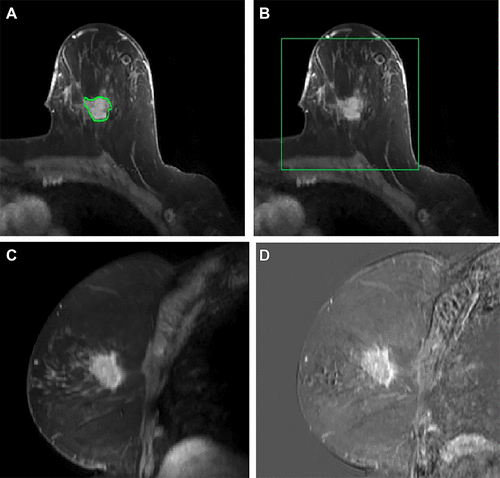
This model, being an adjunct to standard imaging techniques, also has the potential to alleviate the stress and financial burden of further tests for many patients. This study is part of ongoing efforts at UT Southwestern to enhance breast cancer imaging and develop predictive tools for detecting metastasis. The researchers are now focusing on further improving the image analysis process and aim to incorporate a broader array of data to confirm their results.
“That’s an important advancement because surgical biopsies have side effects and risks, despite having a low probability of a positive result confirming the presence of cancer cells,” said study leader Basak Dogan, M.D., at UT Southwestern “Improving our ability to rule out axillary metastasis during a routine MRI – using this model – can reduce that risk while enhancing clinical outcomes.” The findings of the study were published in the journal Radiology: Imaging Cancer on April 12, 2024.
Related Links:
UT Southwestern Medical Center