MRI Aids Physicians in Diagnosing Early Liver Disease
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 17 Aug 2016
A safe, non-invasive 15-minute magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan can eliminate unnecessary biopsies for liver assessment.Posted on 17 Aug 2016
LiverMultiScan is a non-invasive medical imaging software tool, which uses MRI data to calculate proton density fat fraction, T2, and T1 in the liver, which correlate histologically with steatosis, hemosiderosis, and fibrosis of the liver. T1 and T2 are physical parameters, which describe the ‘relaxivity’ of tissue in an induced magnetic field. The strong magnetic field in an MRI machine is used to excite water and fat molecules which – depending on their local environment – relax at different speeds. As they relax, they emit a signal, which is used to create the T1 and T2 MR images.
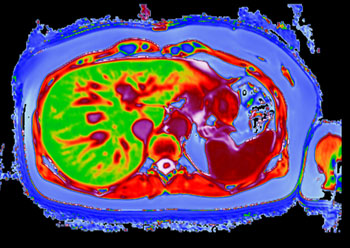
Image: A LiverMultiScan image of a post-bariatric liver (Photo courtesy of Perspectum Diagnostics).
T2 is influenced by iron deposits, which act as small magnets, causing signal decay at a rate proportional to the iron concentration. Tissues with high iron typically have very small T2’s, whilst tissues with very low iron have high T2’s; it can therefore be used as a biomarker in the assessment of hepatic iron overload (hemosiderosis). T1 is influenced by the type and structural organization of a tissue; denser tissues such as fat have very low T1’s, whilst tissues with a high water content such as muscle and spleen have very high T1’s.
T1 is thus useful as a biomarker the assessment of myocardial fibrosis. But since more than 40% of liver disease patients have iron overload, T1 values are distorted, increasing the risk of misdiagnosis. The T2 image is thus used to correct for iron, producing a proprietary metric called cT1, which be used to identify and treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). LiverMultiScan was developed by Perspectum Diagnostics (Oxford, United Kingdom), and is marketed by Mirada Medical (Oxford, United Kingdom).
The Kids4LIFe consortium has been awarded a €1.1million grant to develop and validate LiverMultiScan specifically for patients under 16, which could save them from having to undergo biopsies. As part of the project, a cloud-based health data management system will be developed by the Polish telemedicine company Silvermedia (Krakow, Poland) which will allow rapid transfer of liver scans, as well as other health information and diagnostic test results, between local pediatricians and experts in other cities and countries.
“Liver biopsy is important for making diagnosis of various liver diseases and is frequently used in follow up to make decisions on therapy. We try to decrease indications for liver biopsy in children because it can cause complications and needs sedation and anesthesia,” said Professor Piotr Socha, of Children's Memorial Health Institute (Warsaw, Poland), where the clinical trial will be held.
Related Links:
Perspectum Diagnostics
Mirada Medical
Silvermedia