Portable Multi-modal Medical Imaging System Offers Solution for Emergency Medical Rescue
Posted on 05 Dec 2024
The world’s growing population and expansive territories are increasingly vulnerable to frequent natural disasters, driven by complex geographical and climatic conditions. Earthquakes, floods, and typhoons are common disasters that threaten lives and property globally. In response, many governments have prioritized disaster prevention and mitigation by forming international rescue teams. Following significant disasters, social relief organizations have also participated in rescue efforts, and relevant standards and specifications have been issued to enhance rescue capabilities worldwide.
Emergency medical rescue is aimed at various emergencies, characterized by suddenness, complexity, urgency, harsh environment, and danger. Distinct from in-hospital first aid, it places a stronger emphasis on professionalism, organization, and teamwork. War injury rescue, a critical category of emergency medical care, often occurs under the threat of enemy fire and involves a diverse array of wound types. Most war-injured die before reaching a medical facility because of severe hemorrhage. Effective management of hemorrhage, optimization of airway management, or reducing the time between the point of injury and surgical intervention are crucial in improving combat casualty outcomes. The "4R" principle—Right Time, Right Place, Right Care, and Right Patient—has been proposed as a guideline for combat casualty rescue. Different emergency rescue types require different approaches, but the key objective remains to diagnose and treat casualties quickly and accurately.
Introduction to multi-modal imaging diagnostic technology
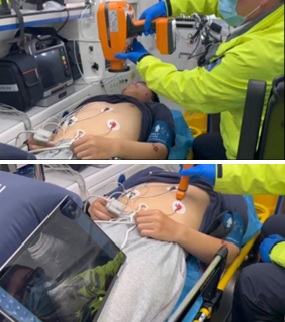
At the rescue scene, injury classification is the primary task, with portable medical instruments favored for their flexibility and efficiency. Targeted imaging technologies and equipment are utilized based on the specific medical imaging needs of various conditions. Doctors select appropriate imaging tools according to the patient’s condition and the location of the lesion, often combining multiple imaging modalities to achieve more accurate diagnostic results. Multi-modal medical imaging technology is a technique that integrates digital radiography (DR) systems and ultrasound imaging systems into a single software-controlled platform. By addressing the limitation of separate operation for DR and ultrasound systems, this innovation allows simultaneous control of both systems through a single software interface, streamlining the diagnostic process in emergency and rescue scenarios.
The portable multi-modal medical imaging system from SIUI (Shantou, China) integrates portable DR and portable color Doppler ultrasound to deliver comprehensive imaging solutions for emergency medical situations. By integrating these two advanced imaging modalities, the system enables detailed assessments of internal organs, bones, and soft tissues, offering critical insights into patient injuries. The dual imaging methods can mutually confirm with each other, enhancing diagnostic accuracy by providing more complete and corroborative imaging data for on-site medical rescue efforts. In addition, the ability to quickly switch between the two examination modes on the same operating system reduces the need for coordinating multiple pieces of equipment in emergency settings, saving both manpower and resources
Advantages of portable multi-modal medical imaging systems
The portable X-ray generator delivers high-precision images with minimal radiation leakage, while the digital flat panel detector utilizes weak current excitation technology, enabling highly sensitive detection and imaging even at low radiation doses. With various exposure modes, including wireless control, and support for both wired and wireless connections, the system ensures excellent imaging performance across diverse applications. The portable color Doppler ultrasound system features easy operation with graphical indications, allowing for fast, standardized workflow (E-FAST). It is powered by a built-in lithium battery that offers long battery life and supports both wired and wireless connections. Additionally, the intuitive and customizable workflow enhances user experience, making it accessible and efficient for a variety of applications.
The system has been demonstrated in studies to effectively rule out visceral damage through ultrasound while identifying metallic fragments with DR imaging, guiding subsequent surgical intervention. This timely and accurate assessment greatly improved the chances of a successful outcome, showcasing the system's value in emergency medical situations. Portable multi-modal medical imaging systems enhance emergency rescue by improving screening accuracy, increasing rescue efficiency, and optimizing treatment plans. Despite their revolutionary potential, the application value of these systems is often underappreciated. Further research is essential to enhance service quality in emergency treatment and expand their role across various application fields.
Authors: Xin Cai , Bohan Li , Xurui Zeng, Shengjie Lin, Liangxia Shu, Jiaxuan Zeng
[1] Yue Maoxing, LIU Zhiguo, Lin Hongwei, LI Jianzhong, Hua Nan. The main characteristics and principles of medical emergency rescue at the scene of disaster accidents[J] J General Medicine,2004,7(18): 1327-1329.
[2] Eastridge B J,Mabry R L,Seguin P,et al. Death on the battlefield (2001-2011): Implications for the future of combat casualty care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012 Dec;73(6 Suppl 5):S431-S437. https://journals.lww.com/jtrauma/abstract/2012/12005/death_on_the_battlefield__2001_2011 ___implications.10.aspx
[3] Yao Xiao, Yang Tingyi. Key Points of the US Army's 2021 Tactical Combat Injury Treatment Guide Update and Enlightenment [J]. Chinese Disaster Relief Medicine,2022, 10 (5): 268-272.
[4] Ma Xiaoxuan, Zhou Hua, Sun Peng, et al. Analysis on the application of portable digital X-ray examination in 95 soldiers of a basic-level army [J]. People Journal of Military Medicine, 2019,63(4):329-331.
[5] Williams CA,Miller KE,WilliamsNP,et al. Distribution and co-expression of adrenergic receptor-encoding mRNA in the mouse inferior colliculus[J].Comp Neurol,2021,529(8):1743-1755.
[6] Giovanni Verlini.International Atomic Energy Agency. Haiti earthquake update 3: mobile x-ray units reach destination [N/OL].
[7] Alejandro Cardozo*,Federico Puerta,Libardo Valencia. E-FAST:A propos of hemopericardium in the Emergency Department[J]. Journal of Acute Disease,2016,5(3):260-263.
Related Links: SIUI