AI Outperforms Radiologists in Detecting Tiny Brain Hemorrhages on CT Scans
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 02 Jan 2020
Scientists at UC San Francisco (San Francisco, CA, USA) and UC Berkeley (Berkeley, CA, USA) have developed an algorithm that performed better than two out of four expert radiologists in finding tiny brain hemorrhages in head scans. The algorithm could help doctors treat patients with traumatic brain injuries (TBI), strokes and aneurysms.Posted on 02 Jan 2020
Radiologists have to look at thousands of images each day, searching for tiny abnormalities that can signal life-threatening emergencies. Some spots may be on the order of 100 pixels in size, in a 3D stack of images containing over a million of them, and even expert radiologists sometimes miss them, with potentially grave consequences. However, radiologists could be much more efficient and accurate if artificial intelligence (AI) technology can pick out the images with significant abnormalities, so they can be examined more closely.
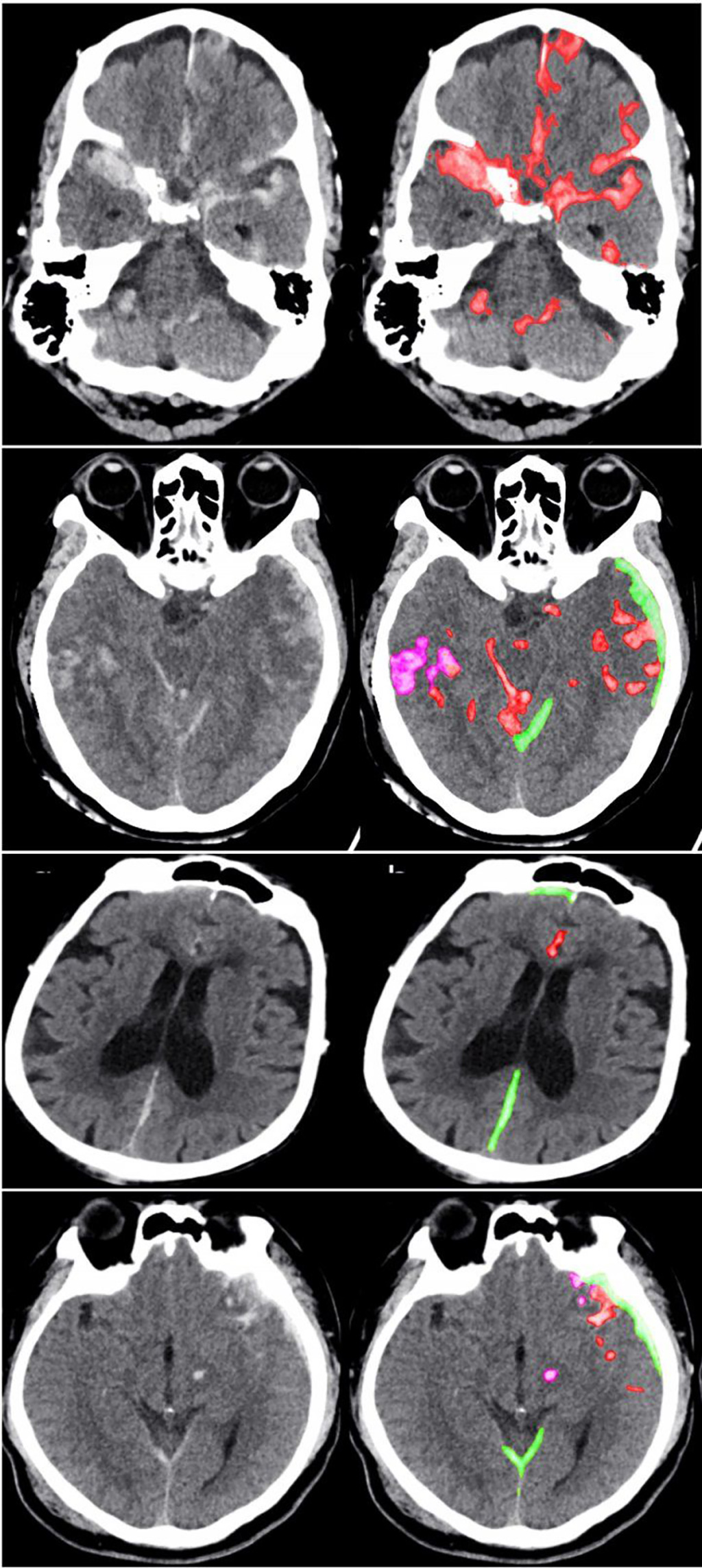
Image: CT scans of the head (Photo courtesy of UC San Francisco)
The algorithm developed the UCSF researchers took just one second to determine whether an entire head scan contained any signs of hemorrhage. It also traced the detailed outlines of the abnormalities it found – demonstrating their location within the brain’s 3D structure. The algorithm found some small abnormalities that the experts missed. It also noted their location within the brain, and classified them according to subtype, information that physicians need to determine the best treatment. Notably the algorithm provided all of this information with an acceptable level of false positives – minimizing the amount of time that physicians would need to spend reviewing its results. The radiology experts said the algorithm’s ability to find very small abnormalities and demonstrate their location in the brain was a substantial advance.
“The hemorrhage can be tiny and still be significant,” said Pratik Mukherjee, MD, PhD, professor of radiology at UCSF. “That’s what makes a radiologist’s job so hard, and that’s why these things occasionally get missed. If a patient has an aneurysm, and it’s starting to bleed, and you send them home, they can die."
Related Links:
UC San Francisco
UC Berkeley














