Deep Learning Technique Could Reveal Transparent Features in Medical Images
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 31 Dec 2018
Engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Cambridge, MA, USA) have developed a deep learning technique that can reveal images of transparent features or objects that are nearly impossible to decipher in almost total darkness.Posted on 31 Dec 2018
Deep neural networks have been widely applied in the field of computer vision and image recognition. The MIT engineers recently developed neural networks to reconstruct transparent objects in images taken with plenty of light. However, they became the first to use deep neural networks in experiments to reveal invisible objects in images taken in the dark.
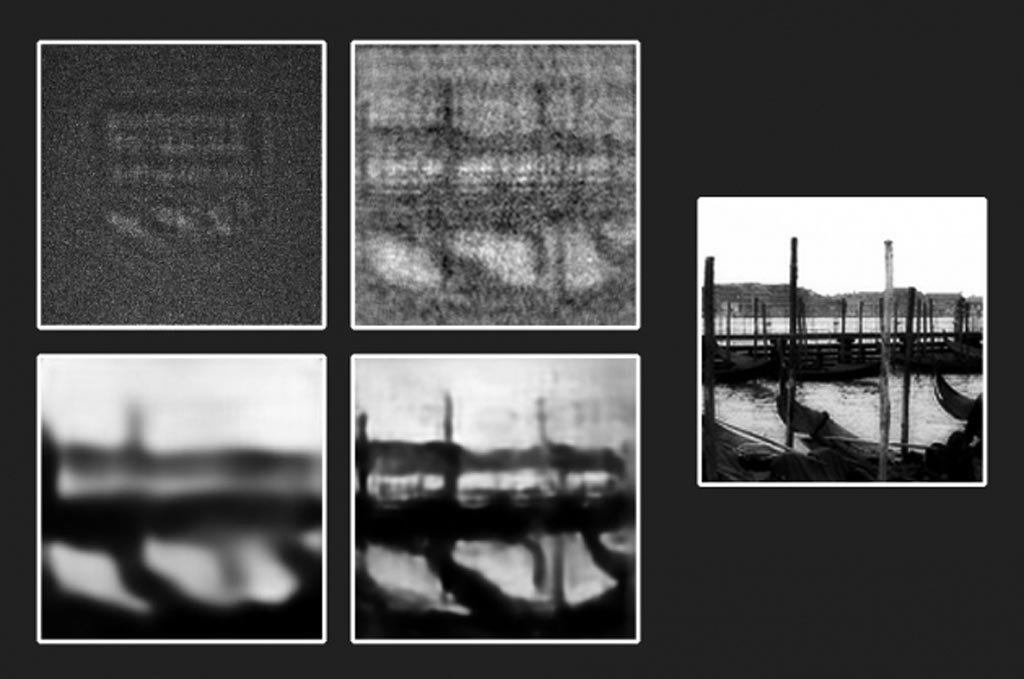
Image: From an original transparent etching (far right), engineers produced a photograph in the dark (top left), then attempted to reconstruct the object using first a physics-based algorithm (top right), then a trained neural network (bottom left), before combining both the neural network with the physics-based algorithm to produce the clearest, most accurate reproduction (bottom right) of the original object (Photo courtesy of MIT).
In their study, the researchers reconstructed transparent objects from images of those objects, taken in almost pitch-black conditions using a “deep neural network.” This machine-learning technique involves training a computer to associate certain inputs with specific outputs — in this case, dark, grainy images of transparent objects and the objects themselves.
The researchers trained a computer to recognize more than 10,000 transparent glass-like etchings, based on extremely grainy images of those patterns. The images were taken in very low lighting conditions, with about one photon per pixel — far less light than a camera would register in a dark, sealed room. They then showed the computer a new grainy image, not included in the training data, and found that it learned to reconstruct the transparent object that the darkness had obscured.
The researchers repeated their experiments with a totally new dataset, consisting of more than 10,000 images of more general and varied objects, including people, places, and animals. After training, the researchers fed the neural network a completely new image, taken in the dark, of a transparent etching of a scene with gondolas docked at a pier. The once again found that the physics-informed reconstruction produced a more accurate image of the original, compared to reproductions without the physical law embedded. The results demonstrate that deep neural networks can be used to illuminate transparent features such as biological tissues and cells, in images taken with very little light.
“We have shown that deep learning can reveal invisible objects in the dark,” said the study’s lead author Alexandre Goy. “This result is of practical importance for medical imaging to lower the exposure of the patient to harmful radiation, and for astronomical imaging.”
Related Links:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology














