AI Software for Restoring Photos Could Find Use in Medical Imaging
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 16 Aug 2018
Researchers have developed a deep learning-based approach that can fix photos originally taken in low light and are grainy or pixilated, and automatically remove the noise and artifacts by simply looking at examples of corrupted photos only. The approach can also be used to enhance MRI images, which could pave the way for a drastic improvement in medical imaging.Posted on 16 Aug 2018
Researchers from NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), Aalto University (Espoo, Finland), and MIT (Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA), presented their work at the recent International Conference on Machine Learning held in Stockholm, Sweden.
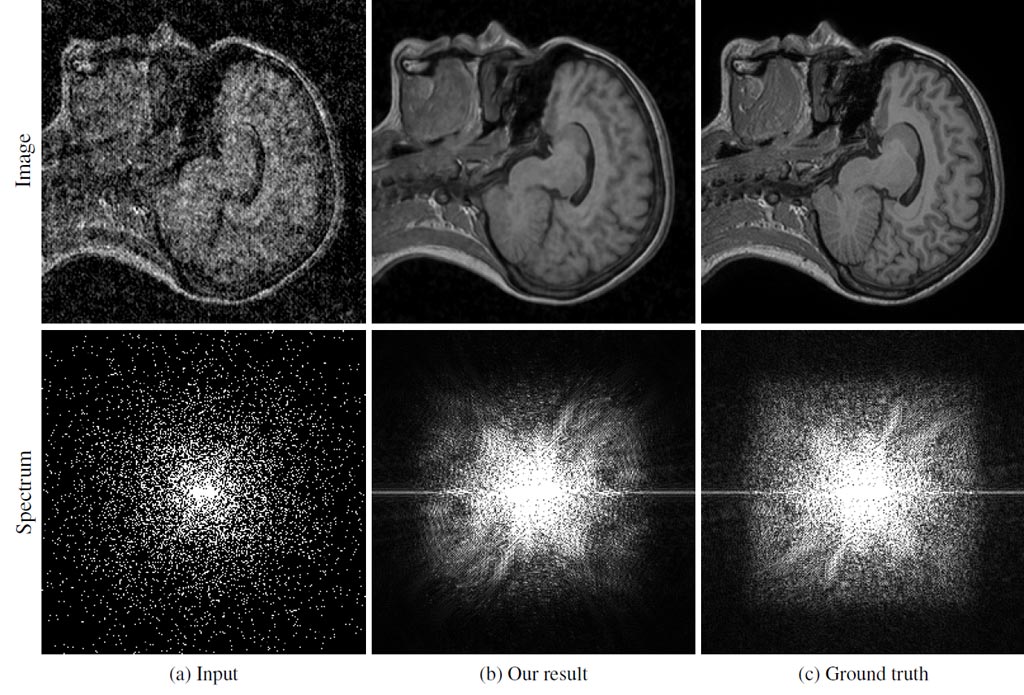
Image: MRI reconstruction example. (a) Input image with only 10% of spectrum samples retained and scaled by 1/p. (b) Reconstruction by a network trained with noisy target images similar to the input image. (c) Original, uncorrupted image (Photo courtesy of NVIDIA).
Recent work on deep learning in the field has been focused on training a neural network to restore images by showing example pairs of noisy and clean images, with the AI then proceeding to learn how to make up the difference. This method is different from the one developed by the researchers as it requires only two input images with noise or grain. Using NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs with the cuDNN-accelerated TensorFlow deep learning framework, the researchers trained their system on 50,000 images in the ImageNet validation set. The team tested the system by validating the neural network on three different datasets. The new AI can remove artifacts, noise, grain, and automatically enhance photos without being shown what a noise-free image looks like.
“It is possible to learn to restore signals without ever observing clean ones, at performance sometimes exceeding training using clean exemplars,” the researchers stated in their paper.“ [The neural network] is on par with state-of-the-art methods that make use of clean examples — using precisely the same training methodology, and often without appreciable drawbacks in training time or performance.”
“There are several real-world situations where obtaining clean training data is difficult: low-light photography (e.g., astronomical imaging), physically based rendering, and magnetic resonance imaging,” the team said. “Our proof-of-concept demonstrations point the way to significant potential benefits in these applications by removing the need for potentially strenuous collection of clean data. Of course, there is no free lunch – we cannot learn to pick up features that are not there in the input data – but this applies equally to training with clean targets.”




 Guided Devices.jpg)









