Study Shows How Deep Learning and AI Diagnose TB
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 24 Apr 2017
Researchers have found that they can use an artificial intelligence technique called deep learning to identify cases of tuberculosis on chest X-Ray exams with a net accuracy rate of 96%.Posted on 24 Apr 2017
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) around 1.8 million people died from tuberculosis (TB) in 2016. A simple chest X-Ray exam can help radiologists identify the disease, but many TB patients live in remote areas without access to expert radiologists who can interpret the images, and diagnose the disease.
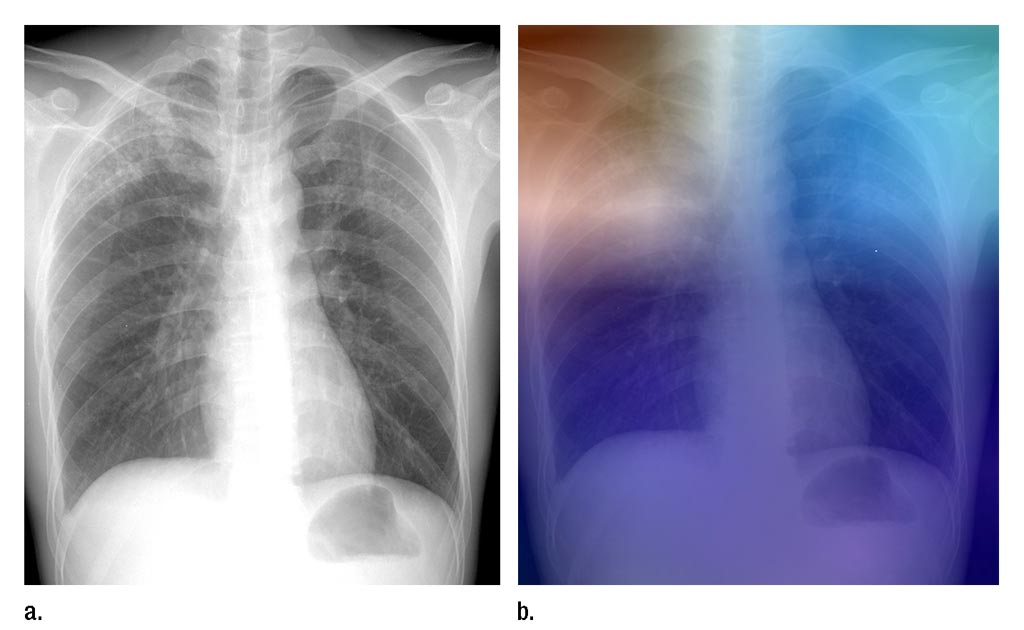
Image: A chest X-Ray of a patient with active TB, and an X-Ray with a heat map overlay showing some of the results of the AI analysis (Photo courtesy of RSNA).
The study was carried out by researchers at the Thomas Jefferson University Hospital who trained artificial intelligence models to identify TB on chest X-rays. The goal of the research was to help screen and evaluate patients in TB-prevalent areas lacking access to radiologists. The study was published in the April 25, 2017, online issue of the journal Radiology.
The researchers used 1,007 X-Ray exams of patients with and without active TB for the study. The multiple TB-positive and TB-negative X-Ray datasets were used to train two different Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) models called AlexNet and GoogLeNet. The researchers found that the best performing Artificial Intelligence (AI) model was when both AlexNet and GoogLeNet were used together, resulting in a net accuracy of 96%.
Co-author of the study, Paras Lakhani, MD at TJUH, said, “There is a tremendous interest in artificial intelligence, both inside and outside the field of medicine. An artificial intelligence solution that could interpret radiographs for presence of TB in a cost-effective way could expand the reach of early identification and treatment in developing nations. The relatively high accuracy of the deep learning models is exciting. The applicability for TB is important because it’s a condition for which we have treatment options. It’s a problem that can be solved. We hope to prospectively apply this in a real world environment. An artificial intelligence solution using chest imaging can play a big role in tackling TB.”













