New Software Used to Correct Metal Artifacts in CT Images
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 29 Dec 2016
Researchers in the US have compared the ability of iMAR, dual-energy virtual monochromatic imaging, and a combined technique, to correct imaging artifacts resulting from metal orthopedic and dental implants.Posted on 29 Dec 2016
Iterative Metal Artifact Reduction (iMAR), and dual-energy virtual monochromatic imaging, are two software techniques that clinicians use to compensate for artifacts created by metal implants during Computed Tomography (CT) imaging scans.
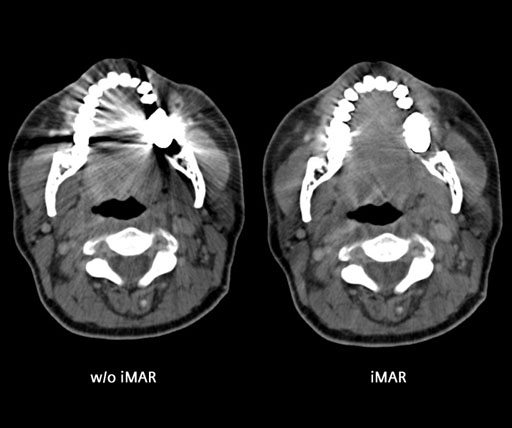
Image: An example of the application of iterative Metal Artifact Reduction (iMAR) in CT imaging (Photo courtesy of University Erlangen Radiologie, Erlangen, Germany).
The researchers from the Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN, USA) also used a third technique that combines iMAR and virtual monochrome imaging. The metal artifact reduction software can be used directly from the CT scanner console. Each implant type causes different artifacts. For example, the metal in tooth fillings and artificial joints can block CT from imaging surrounding tissue, and can cause beam hardening, beam scattering, non-linear partial volume effects, and photon starvation. The results are severe streaking and shadows on the CT scans that prevent radiologists from accurately reading the images.
The results were presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA2016), and showed that iMAR was better at eliminating artifacts for implants of the hip and knee, while for dental implants dual-energy virtual monochromatic imaging was more effective. In dental imaging iMAR actually introduced additional artifacts. A combination of both techniques was found most effective for spinal implants.
Medical physicist Lifeng Yu, PhD, at the Mayo Clinic, said, "Metal artifacts are the most challenging unsolved problem in the 40-year history of CT scans. While the processed images are a great improvement over the originals, the techniques are still not perfect, and the final outcome is case by case."
Related Links:
Mayo Clinic














