Scientists Propose New Ultrasound Video Process Using a Wavelet Variational Model
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 17 May 2016
Scientists have developed a new ultrasound video image segmentation model that can be used in medical image analysis to recognize Regions of Interest (ROI) and facilitate the interpretation of ultrasound images.Posted on 17 May 2016
Real-time applications require efficient image segmentation algorithms. Ultrasound videos often suffer from a low contrast level, shadow effects, and complex ‘noise’ statistics.
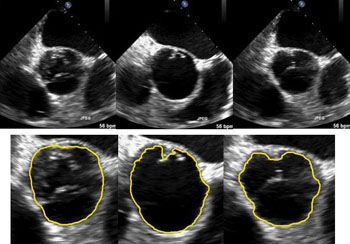
Image: The image shows selected, original, ultrasound images and the results of Region of Interest (ROI) tracking using a wavelet variational model (Photo courtesy of Xiaoqun Zhang).
The research was published online in the April 7, 2016, issue of the SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences and proposes a model for tracking moving boundaries in ultrasound video, using a mathematically sound framework. The model uses wavelet frames and noise statistics under a variational framework. The efficiency of the variational model makes it useful for real-time clinical applications. Such models are commonly used in motion tracking or edge detection, and have been shown to be robust and effective for complex image segmentation tasks. Wavelet frame regularization allowed the scientists to track and sharpen geometric shapes in the videos, while they were segmented automatically through sequential images. The model was designed to segment ultrasound videos sequentially and collectively, and to include shape priors during segmentation of a single image. Consecutive shape priors are then calculated automatically for subsequent segmentations.
Jiulong Liu, PhD student, Department of Mathematics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Shanghai, China), said, "Ultrasound imaging is an important modality in clinical application due to its low cost and portability. However, its related analysis for accurate diagnosis and monitoring is still challenging due to low image quality, artifacts, and noise. The numerical results on real ultrasound data sets demonstrate that the proposed wavelet frame model with distance prior can track the regions of interest effectively, in terms of both segmentation quality and computational time. The results compare favorably with other approaches. The model can be further extended to other imaging modality or to locate multi-region simultaneously. More geometric and prior information can be used to enhance the robustness of the method."
Related Links:
Shanghai Jiao Tong University














