Automated Angiography Analysis System Detects Severe CAD in Real-Time
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 10 Dec 2009
A coronary computerized tomography angiography (cCTA) analyzer system automatically processes acquired images, helping to rule out coronary artery stenosis in emergency department (ED) patients with chest pains.Posted on 10 Dec 2009
Researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (Boston, MA, USA) conducted a retrospective study of images garnered from cCTAs of 115 low to intermediate risk patients who entered the emergency department (ED) with suspected coronary artery disease (CAD), and compared the analyses of the cCTA studies with the interpretation by consensus opinion of two expert readers who served as the gold standard. The results showed that in 100 analyzable studies, the automated results from the analyzer system yielded a negative predictive value (NPV) of 98%. The system also identified five of six patients determined by the expert readers to have significant stenosis, for a sensitivity of 83% and a specificity of 82%. The study was presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), held during November-December 2009 in Chicago (IL, USA).
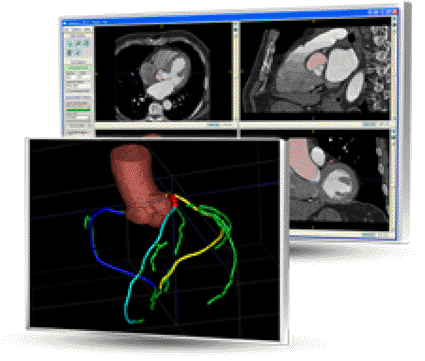
Image: Rcadia COR Analyzer automated analysis of CCTA studies (Photo courtesy of Rcadia Medical Imaging).
"In recent years, cCTA has proven to be an effective, noninvasive procedure for coronary artery analysis,” said principal investigator radiologist Girish Tyagi, M.D. "However, coronary CT angiography is under-utilized in the ED because the procedure relies on expert readers who may not be immediately available during ‘off hours'. In our study, we asked whether this fully automated software tool could assist in patient triage by comparing the automated results with those of expert readers.”
The system used for the study was the COR Analyzer System, a product of Rcadia Medical Imaging (Haifa, Israel), which utilizes images from 64-slice or higher CT machines to generate comprehensive results and corresponding reports within minutes. The system's algorithm determines the presence of significant lesions--more than 50% stenosis--in the coronary arteries and visualizes the results to indicate the location of candidate lesions in real-time. The findings can be easily verified and validated using simple visualization tools including standard two dimensional (2D) projections, schematic three-dimensional (3D) images, and curved multi-planar reconstruction (MPR) views. The ability of the automated system to enhance the use of cCTA has potential to significantly reduce unnecessary utilization of coronary observation beds in the low to moderate probability CAD patient.
Related Links:
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Rcadia Medical Imaging














