CT Modeling Can Simulate Intracardiac Flow Patterns
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 02 Aug 2018
A new study shows that blood flow patterns derived from cardiac four-dimensional (4D) computerized tomography (CT) scans are similar to those derived from 4D flow magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).Posted on 02 Aug 2018
Researchers at Linköping University (LIU; Sweden) conducted a study in 12 participants (mean age 57 years; seven men) in order to investigate if flow simulations based solely on CT-derived cardiac anatomy were comparable to 4D flow MRI. With the aid of modeling methods designed to simulate fluid flow and turbulence in aeronautical and motor industries, the researchers assessed blood flow in a patient’s heart with the aid of high-resolution CT images. To compile the massive data sets, they used supercomputers at the Swedish National Supercomputer Centre (NSC) at LiU.
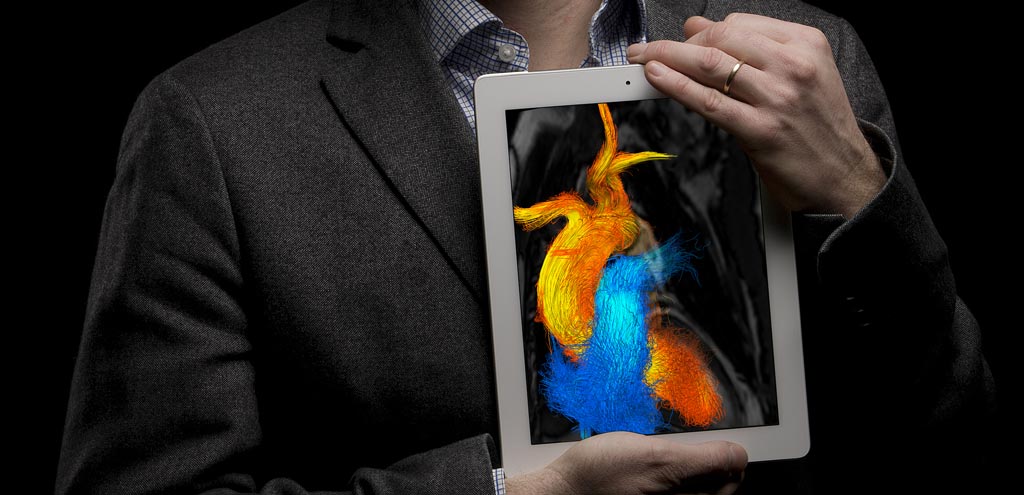
Image: Cardiac flow patterns can now be derived from CT alone (Photo courtesy of Oscar Luren / LiU).
Flow patterns and rates, stroke volume, kinetic energy, and flow components were quantified for both techniques, and then compared. The results revealed that cardiac flow patterns were qualitatively and quantitatively akin to 4D flow MRI measurements, as graded by three independent observers. Peak flow rate, stroke volumes, and integrated kinetic energy at peak systole showed high correlation, but kinetic energy levels at early and late filling did not correlate. There was also a high correlation for direct and residual components, but retained and delayed components showed no such correlation. The study was published on June 26, 2018, in Radiology.
“This is the first time we have shown that we can simulate the function of the heart in a particular patient. In the future, we won’t need to use supercomputers: the calculations can be done at the CT scanner,” said study co-author professor of applied thermodynamics and fluid mechanics Matts Karlsson, PhD, director of NSC. “This is a good example of how we manage the infrastructure we have at LiU, with magnetic resonance cameras, computer tomographs, and supercomputers. We don’t sit in our own isolated rooms: it’s easy to carry out cross-disciplinary research at LiU.”
“Magnetic resonance cameras are effective, but they are not available everywhere. The investigation is expensive, patients should not have any metal like pacemakers in their body, and the investigation takes quite some time,” added senior author professor of cardiovascular medicine Tino Ebbers, MD. “Since CT scanning is quick and easy, we can reach completely new patient groups. We can now simulate how the heart is functioning in individual patients.”
Related Links:
Linköping University