Smoking, Age and Diabetes Linked to Hippocampal Calcifications
By MedImaging International staff writers
Posted on 12 Jul 2018
A new multiplanar computerized tomography (CT) study shows that older age, diabetes mellitus, and smoking are associated with an increased risk of hippocampal calcifications.Posted on 12 Jul 2018
Researchers at University Medical Center Utrecht (UMCU; The Netherlands) and Tergooi Hospital (Hilversum, The Netherlands) conducted a study in 1,991 patients (average age 78 years), who visited the memory clinic at Tergooi Hospital between 2009 and 2015. All patients had a standard diagnostic workup, including cognitive tests and brain CT scans, which were analyzed for presence and severity of hippocampal calcifications. The researchers then studied their association with vascular risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes and smoking, and also assessed the effects of calcifications on cognitive function.
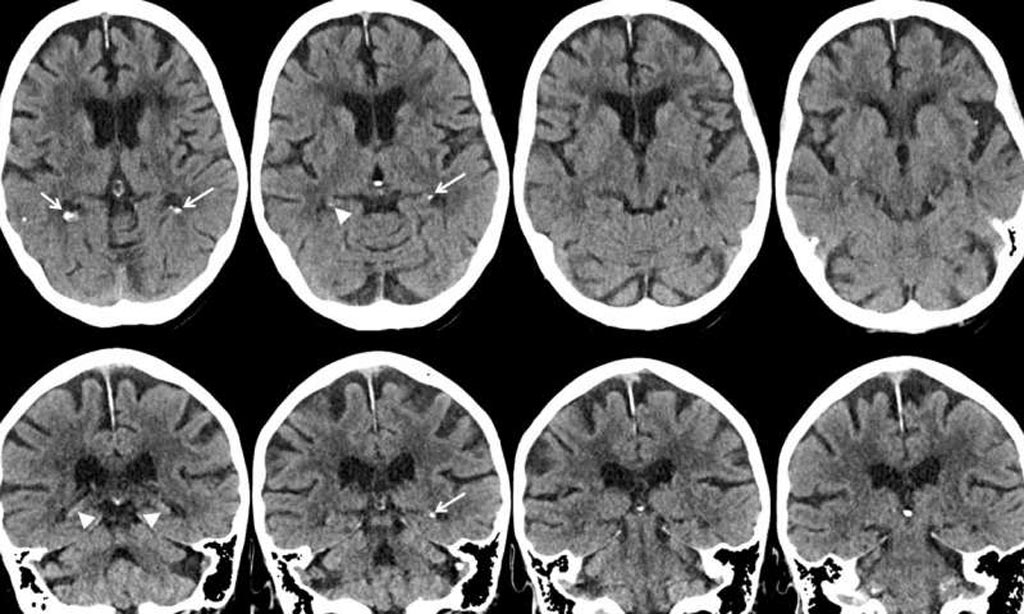
Image: Axial and coronal CT images show mild hippocampal calcification (arrowheads) (Photo courtesy of RSNA).
The results revealed that 19.1% of the patients had hippocampal calcifications. Older age, diabetes mellitus, and smoking were associated with the presence of hippocampal calcifications, but no link was found between the presence and severity of hippocampal calcifications and cognitive function. As a result, the researchers plan to carry out additional studies in different groups of people to better understand possible connections between hippocampal calcifications and cognitive problems. The study was published on June 12, 2018, in Radiology.
“We do think that smoking and diabetes are risk factors. In a recent histopathology study, hippocampal calcifications were found to be a manifestation of vascular disease,” said lead author Esther JM de Brouwer, MD, a geriatrician at UMCU. “It is well known that smoking and diabetes are risk factors for cardiovascular disease. It is therefore likely that smoking and diabetes are risk factors for hippocampal calcifications.”
“Multiplanar CT scan makes it possible to see the hippocampus in different anatomical planes; for example, from top to bottom, right to left, and front to back,” concluded Dr. de Brouwer.”Before multiplanar CT scans, hippocampal calcifications were often mistaken for choroid plexus calcifications. So with multiplanar CT scans, hippocampal calcifications are better distinguished from calcifications in other areas.”
Hippocampal calcifications were first described in a pathology study in 2002 as a vasculopathy with fibrosis and calcifications with a predilection for the middle hippocampal artery. These calcifications can spread from the tail to the body of the hippocampus and occasionally to the head, and may lead to patchy neuronal loss. Accordingly, it has been hypothesized that hippocampal calcifications may be a manifestation of vascular abnormalities that could contribute to hippocampal atrophy and cognitive deterioration, such as in dementia.
Related Links:
University Medical Center Utrecht
Tergooi Hospital














