Dual-Source CT Has Fast Scans and Low Radiation Dose for Cardiac Applications
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 29 Apr 2009 |
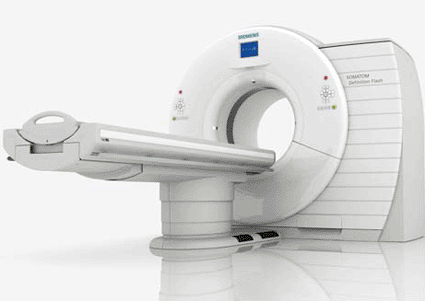
Image: The Somatom Definition Flash dual-source CT scanner (Photo courtesy of Siemens Healthcare).
A dual-source computed tomography (CT) system provides flexible cardiac examinations with a minimum radiation dose.
Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) presented very fast speed and lowest dose radiation for cardiac applications with the Somatom Definition Flash dual-source CT scanner at the 58th annual scientific session of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) in March 2009, in Orlando, FL, USA. Siemens CT covers the entire spectrum of cardiology, from early detection to acute care through follow-up.
"The Somatom Definition Flash requires only a fraction of the radiation dose that systems previously required to scan even the tiniest anatomical details faster than ever before," said Kulin Hemani, vice president, CT, Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc. "Scanning the thorax, including the heart, can be done in only 0.6 seconds, taking the burden of breath-holding off the patient and allowing functional imaging for body regions up to 48 cm."
Temporal resolution of 75 ms and scan speed of up to 43 cm/s make heart-scanning possible, with dose levels below 1 millisievert (mSv), whereas the average effective dose required for this purpose usually ranges from 8 mSv to 40 mSv. The patient is moved through the CT-scanner more than twice as fast as with any traditional system, and at the same time, requiring a much lower radiation dose than conventional scans. In comparison, the X-ray radiation that the average person is exposed to each year from natural sources amounts to 2-5 mSv. The dose values of the new Siemens CT scanner lie far below those of an intracardiac catheter examination, thus opening up possibilities for using CT scanners for routine cardiologic examinations.
A scan of the entire heart can be performed in only 250 milliseconds, which is less than half a heartbeat. Moreover, it is possible for physicians to effectively display a heart with a fast pulse or an irregular heart beat without using beta blockers, thus simplifying the workflow and yielding clinical and financial advantages. The Somatom Definition Flash is the only CT scanner on the market that enables the use of noninvasive cardiologic diagnostic techniques as routine applications at the lowest possible radiation exposure levels.
The second generation of dual energy imaging will introduce a new imaging quality. The contrast in CT scans will be increased without having to apply the higher radiation dose previously required. This is achieved via a new, selective photon shield that blocks unnecessary parts of the energy spectrum. It thereby provides improved separation of the two simultaneous scans with low and high photon energy, without causing a higher radiation exposure than would result from an individual, conventional CT examination with only one energy source. Thus, the system can always provide a double contrast that, for the first time ever, can also be used to classify the chemical composition of tissues via a CT scan in routine daily work.
Another technical development for keeping the patient's radiation exposure as low as possible is the X-Care application. For the first time ever, this application selectively reduces the radiation exposure of dose-sensitive anatomical regions, such as the female breast. This is done by switching the X-ray tube assemblies off during the rotation phase in which the anatomical regions concerned are most directly exposed to radiation. In this way, it is possible to reduce the radiation exposure of individual anatomical regions by up to 40%.
Furthermore, an adaptive dose shield blocks irrelevant prespiral and postspiral radiation with dynamic diaphragms, thus ensuring that only a minimum and clinically essential radiation exposure occurs. This enables an additional 25% reduction of the dose required for routine examinations. The Care Dose4D (four dimensional) software, which analyzes the individual cross-sectional anatomy in real time and adapts the emitted X-ray dose accordingly, also helps to reduce radiation exposure.
In addition, Siemens CT Acute Care Engine provides a complete clinical portfolio for imaging emergency patients from head to toe. Using fast, direct 3D reconstruction, images can be reviewed before the patient is off the table. The Somatom Definition Flash, in combination with CT Acute Care Engine, streamlines clinical workflow for cardiac, vascular, musculoskeletal, and stroke evaluation, turning data into diagnostic outcomes within minutes. By combining CT scanner features and programs, solutions can be designed to meet and exceed a site's acute care needs.
Related Links:
Siemens Healthcare
Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) presented very fast speed and lowest dose radiation for cardiac applications with the Somatom Definition Flash dual-source CT scanner at the 58th annual scientific session of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) in March 2009, in Orlando, FL, USA. Siemens CT covers the entire spectrum of cardiology, from early detection to acute care through follow-up.
"The Somatom Definition Flash requires only a fraction of the radiation dose that systems previously required to scan even the tiniest anatomical details faster than ever before," said Kulin Hemani, vice president, CT, Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc. "Scanning the thorax, including the heart, can be done in only 0.6 seconds, taking the burden of breath-holding off the patient and allowing functional imaging for body regions up to 48 cm."
Temporal resolution of 75 ms and scan speed of up to 43 cm/s make heart-scanning possible, with dose levels below 1 millisievert (mSv), whereas the average effective dose required for this purpose usually ranges from 8 mSv to 40 mSv. The patient is moved through the CT-scanner more than twice as fast as with any traditional system, and at the same time, requiring a much lower radiation dose than conventional scans. In comparison, the X-ray radiation that the average person is exposed to each year from natural sources amounts to 2-5 mSv. The dose values of the new Siemens CT scanner lie far below those of an intracardiac catheter examination, thus opening up possibilities for using CT scanners for routine cardiologic examinations.
A scan of the entire heart can be performed in only 250 milliseconds, which is less than half a heartbeat. Moreover, it is possible for physicians to effectively display a heart with a fast pulse or an irregular heart beat without using beta blockers, thus simplifying the workflow and yielding clinical and financial advantages. The Somatom Definition Flash is the only CT scanner on the market that enables the use of noninvasive cardiologic diagnostic techniques as routine applications at the lowest possible radiation exposure levels.
The second generation of dual energy imaging will introduce a new imaging quality. The contrast in CT scans will be increased without having to apply the higher radiation dose previously required. This is achieved via a new, selective photon shield that blocks unnecessary parts of the energy spectrum. It thereby provides improved separation of the two simultaneous scans with low and high photon energy, without causing a higher radiation exposure than would result from an individual, conventional CT examination with only one energy source. Thus, the system can always provide a double contrast that, for the first time ever, can also be used to classify the chemical composition of tissues via a CT scan in routine daily work.
Another technical development for keeping the patient's radiation exposure as low as possible is the X-Care application. For the first time ever, this application selectively reduces the radiation exposure of dose-sensitive anatomical regions, such as the female breast. This is done by switching the X-ray tube assemblies off during the rotation phase in which the anatomical regions concerned are most directly exposed to radiation. In this way, it is possible to reduce the radiation exposure of individual anatomical regions by up to 40%.
Furthermore, an adaptive dose shield blocks irrelevant prespiral and postspiral radiation with dynamic diaphragms, thus ensuring that only a minimum and clinically essential radiation exposure occurs. This enables an additional 25% reduction of the dose required for routine examinations. The Care Dose4D (four dimensional) software, which analyzes the individual cross-sectional anatomy in real time and adapts the emitted X-ray dose accordingly, also helps to reduce radiation exposure.
In addition, Siemens CT Acute Care Engine provides a complete clinical portfolio for imaging emergency patients from head to toe. Using fast, direct 3D reconstruction, images can be reviewed before the patient is off the table. The Somatom Definition Flash, in combination with CT Acute Care Engine, streamlines clinical workflow for cardiac, vascular, musculoskeletal, and stroke evaluation, turning data into diagnostic outcomes within minutes. By combining CT scanner features and programs, solutions can be designed to meet and exceed a site's acute care needs.
Related Links:
Siemens Healthcare
Latest Radiography News
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
- World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
- AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
- Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
- AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Detects Pulmonary Nodules Three Years Before Lung Cancer Symptoms
Channels
MRI
view channel
Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
Aortic stenosis is a common and potentially life-threatening heart condition. It occurs when the aortic valve, which regulates blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body, becomes stiff and narrow.... Read more
New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Individuals with conditions such as diabetes or obesity often experience accelerated aging of their hearts, sometimes by decades.... Read more
AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
Many pediatric gliomas are treatable with surgery alone, but relapses can be catastrophic. Predicting which patients are at risk for recurrence remains challenging, leading to frequent follow-ups with... Read more
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read more
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read more
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read more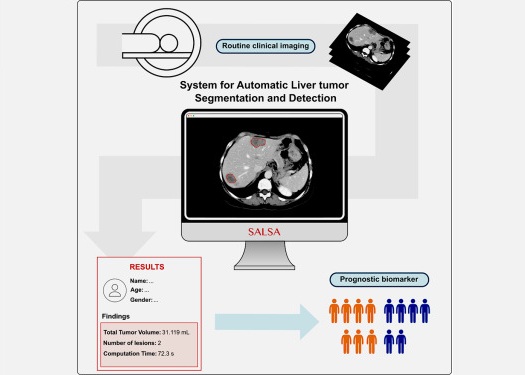
CT-Based Deep Learning-Driven Tool to Enhance Liver Cancer Diagnosis
Medical imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, plays a crucial role in oncology, offering essential data for cancer detection, treatment planning, and monitoring of response to therapies.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more



















